Ginkgo biloba extract improves cognitive function and increases neurogenesis by reducing Aβ pathology in 5×FAD mice
- PMID: 33841671
- PMCID: PMC8014356
Ginkgo biloba extract improves cognitive function and increases neurogenesis by reducing Aβ pathology in 5×FAD mice
Abstract
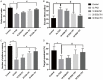
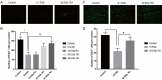
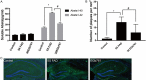
Previous studies have indicated that the generation of newborn hippocampal neurons is impaired in the early phase of Alzheimer's disease (AD). A potential therapeutic strategy being pursued for the treatment of AD is increasing the number of newborn neurons in the adult hippocampus. Recent studies have demonstrated that ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) plays a neuroprotective role by preventing memory loss in many neurodegenerative diseases. However, the extent of EGb 761's protective role in the AD process is unclear. In this study, different doses of EGb 761 (0, 10, 20, and 30 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injections once every day for four months) were tested on 5×FAD mice. After consecutive 4-month injections, mice were tested in learning memory tasks, Aβ, and neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus (DG) of hippocampus and morphological characteristics of neurons in DG of hippocampus. Results indicated that EGb 761 (20 and 30 mg/kg) ameliorated memory deficits. Further analysis indicated that EGb 761 can reduce the number of Aβ positive signals in 5×FAD mice, increase the number of newborn neurons, and increase dendritic branching and density of dendritic spines in 5×FAD mice compared to nontreated 5×FAD mice. It was concluded that EGb 761 plays a protective role in the memory deficit of 5×FAD mice.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ; ginkgo biloba exact; memory; neurogenesis.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® ameliorates cognitive impairment and alleviates TNFα response in 5xFAD Alzheimer's disease model mice.Phytomedicine. 2025 Jan;136:156327. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156327. Epub 2024 Dec 15. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39778487
-
Long-term treatment with Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 improves symptoms and pathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 May;46:121-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 25637484
-
Ginkgo biloba Extract EGb 761 and Its Specific Components Elicit Protective Protein Clearance Through the Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway in Tau-Transgenic Mice and Cultured Neurons.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;65(1):243-263. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180426. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 30010136
-
EGb 761: ginkgo biloba extract, Ginkor.Drugs R D. 2003;4(3):188-93. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200304030-00009. Drugs R D. 2003. PMID: 12757407 Review.
-
[Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761). State of knowledge in the dawn of the year 2000].Ann Pharm Fr. 1999 Jul;57 Suppl 1:1S8-88. Ann Pharm Fr. 1999. PMID: 10481350 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Exploration of natural products for the development of promising cholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease treatment.Heliyon. 2025 Feb 5;11(4):e42479. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42479. eCollection 2025 Feb 28. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40034281 Free PMC article.
-
7-α-O-Methylmorroniside ameliorated brain injury in 5×FAD mice by regulating the gut microbiome and NMDAR2B.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 30;16:1545566. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1545566. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40520172 Free PMC article.
-
Water extract of Humulus japonicus improves age‑related cognitive decline by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase activity and the acetylcholine signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2025 May;31(5):131. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13496. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40116124 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics study to reveal cognitive improvement with treatment of Scrophularia buergeriana.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 23;14(1):17007. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66371-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39043762 Free PMC article.
-
Current Advances in Mitochondrial Targeted Interventions in Alzheimer's Disease.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 22;11(9):2331. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092331. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
