The immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D drops in children with recurrent respiratory tract infections
- PMID: 33841698
- PMCID: PMC8014391
The immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D drops in children with recurrent respiratory tract infections
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of vitamin D drops on immune function in children with recurrent respiratory tract infections (RRTI).
Methods: The clinical data of 119 children with RRTI in our hospital were retrospectively retrieved, and they were divided into group A (n=59, receiving routine treatment) and group B (n=60, receiving vitamin D drops) based on their treatment modality. The clinical efficacy, symptom disappearance time, immune function index, insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 [25-(OH)D3], serum y-interferon (INF-y), and the number of episodes of respiratory tract infections were compared between the two groups.
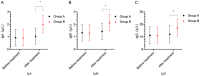
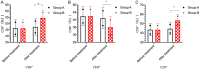
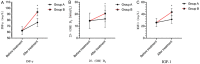
Results: The total effective rate of treatment in group B was 96.67%, which was significantly higher than 71.19% in group A (P<0.05). Children in group B had shorter time to disappearance of lung rales, cough, and fever than group A (P<0.05). Group B had higher IgA, IgG, and IgM levels, higher CD4+, CD3+ levels and lower CD8+ levels as well as higher IGF-1, 25-(OH)D3, INF-y levels, and fewer respiratory infections after treatment than group A (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Vitamin D drops are effective in the treatment of children with RRTI, which is beneficial to the improvement of clinical symptoms and immune function.
Keywords: Recurrent; children; immune function; respiratory tract infections; vitamin D drops.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Okamoto M, Dapat CP, Sandagon AMD, Batangan-Nacion LP, Lirio IC, Tamaki R, Saito M, Saito-Obata M, Lupisan SP, Oshitani H. Molecular characterization of respiratory syncytial virus in children with repeated infections with subgroup B in the philippines. J Infect Dis. 2018;218:1045–1053. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Breuer O, Schultz A, Turkovic L, de Klerk N, Keil AD, Brennan S, Harrison J, Robertson C, Robinson PJ, Sly PD, Ranganathan S, Stick SM, Caudri D. Changing prevalence of lower airway infections in young children with cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200:590–599. - PubMed
-
- Tarantino V, Savaia V, D’Agostino R, Silvestri M, Passali FM, Di Girolamo S, Ciprandi G. Bacteriotherapy in children with recurrent upper respiratory tract infections. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:39–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
