Functional beverages improve insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis modulating lysophospholipids in diet-induced obese rats
- PMID: 33841814
- PMCID: PMC8020945
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2162
Functional beverages improve insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis modulating lysophospholipids in diet-induced obese rats
Abstract
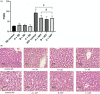
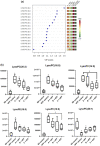
Hypercaloric beverages increase the prevalence of insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), diets with polyphenolic compounds improved these alterations. The study aimed to evaluate the effect of the consumption of three functional beverages (prepared with: Roselle, green tea, cinnamon, Malabar tamarind, and peppermint in different proportions) on insulin resistance and NAFLD and their relation to liver phospholipid regulation in Wistar rats fed with a high-fat and fructose (HFF) diet. The consumption of beverages showed lower liver triglycerides compared to HFF control group, being the called beverage B the successful triggering up to 30.1%. The consumption of functional beverages improved insulin resistance and decreased the abundance of LysoPC (20:2), LysoPC (16:0), LysoPC (14:0), LysoPE (18:0), LysoPC (15:0), and LysoPC (20:1), with beverage C being the one with the meaningful effect. The results indicate that the functional beverage consumption improves insulin resistance, and decrease the degree of NAFLD, these through modifications of lysophosphatidylcholines, and lipids metabolism.
Keywords: NAFLD (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease); functional beverage; insulin resistance; lipids metabolism; lysophospholipids.
© 2021 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Rubio‐Rodríguez Julio C, Reynoso‐Camacho Rosalia, Rocha Guzmán Nuria, and Salgado Luis M. declare that they do not have any conflict of interest. Experiments on animals were performed in accordance with the Animal Care and Use Protocol of the Autonomous University of Queretaro, as recommended by the guidelines for animal testing (NOM‐062‐ZOO‐1999).
Figures

References
-
- Amaya‐Cruz, D. , Peréz‐Ramírez, I. F. , Pérez‐Jiménez, J. , Nava, G. M. , & Reynoso‐Camacho, R. (2019). Comparison of the bioactive potential of Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) calyx and its by‐product: Phenolic characterization by UPLC‐QTOF MSE and their anti‐obesity effect in vivo . Food Research International, 126, 108589. 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108589 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aray, J. , Rodrigo, R. , Videla, L. A. , Thielemann, L. , Orellana, M. , Pettinelli, P. , & Poniachik, J. (2004). Increase in long‐chain polyunsaturated fatty acid n‐6/n‐3 ratio in relation to hepatic steatosis in patients with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clinical Science, 106(6), 635–643. 10.1042/CS20030326 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Askari, F. , Rashidkhani, B. , & Hekmatdoost, A. (2014). Cinnamon may have therapeutic benefits on lipid profile, liver enzymes, insulin resistance, and high‐sensitivity C‐reactive protein in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Nutrition Research, 34(2), 143–148. 10.1016/j.nutres.2013.11.005 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

