Extensor mechanism failure in total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 33841917
- PMCID: PMC8025708
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.6.200119
Extensor mechanism failure in total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
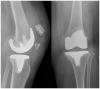
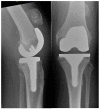
Extensor mechanism failure in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) can present as quadriceps tendon rupture, patella fracture or patella tendon rupture.Component malrotation, excessive joint line elevation and previous lateral release are some of the risk factors contributing to extensor mechanism failure in TKA.Partial quadriceps tendon rupture and undisplaced patella fracture with intact extensor mechanism function can be treated conservatively.Extensor mechanism failure in TKA with disruption of the extensor mechanism function should be treated operatively as it is associated with poor function and extensor lag.It is recommended that acute repair of patella or quadriceps tendon rupture are augmented due to the high risk of re-rupture.Chronic ruptures of the extensor mechanism must be reconstructed as repair has a high failure rate. Reconstruction can be performed using autograft, allograft or synthetic graft. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2021;6:181-188. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.6.200119.
Keywords: patella fracture in total knee arthroplasty; patella tendon rupture in total knee arthroplasty; quadriceps tendon rupture in total knee arthroplasty.
© 2021 The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of interest statement: PJJ reports an educational contract with DePuy Synthes and receives royalties and consultancy fees from DePuy Synthes, outside the submitted work. BVB reports an educational contract with DePuy Synthes and has received speaker fees, outside the submitted work. The other authors declare no conflict of interest relevant to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Schoderbek RJ, Brown TE, Mulhall KJ, et al. . Extensor mechanism disruption after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2006;446:176–185. - PubMed
-
- Bates MD, Springer BD. Extensor mechanism disruption after total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2015;23:95–106. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg AG. Management of extensor mechanism rupture after TKA. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2012;94:116–119. - PubMed
-
- Nam D, Abdel MP, Cross MB, LaMont LE, Reinhardt KR, McArthur BA, et al. . The management of extensor mechanism complications in total knee arthroplasty: AAOS exhibit selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2014;96:e47. - PubMed
-
- Papalia R, Vasta S, D’Adamio S, Albo E, Maffulli N, Denaro V. Complications involving the extensor mechanism after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2015;23:3501–3515. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

