Inhibition of lung cancer by vitamin D depends on downregulation of histidine-rich calcium-binding protein
- PMID: 33842001
- PMCID: PMC8020154
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.08.013
Inhibition of lung cancer by vitamin D depends on downregulation of histidine-rich calcium-binding protein
Abstract
Introduction: Intrinsic vitamin D affects the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, metastasis, and tumorigenesis of lung cancer by regulating tumor signaling pathways. Histidine-rich calcium-binding protein (HRC) maintains Ca2+ homeostasis, which plays crucial roles in the occurrence and development of cancer.
Objectives: Our study aims to investigate the ability of vitamin D in the regulation of HRC and the role of HRC playing in lung cancer.
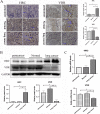
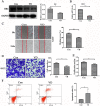
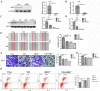
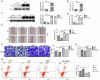
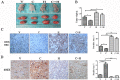
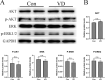
Methods: We investigated the effects of vitamin D on lung cancer and the underlying mechanisms, by measuring HRC and vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression in lung cancer, paracancer, and normal tissues from patients using immunohistochemistry, western blotting, and real time RT-PCR. We transfected H460 lung cancer cells (supplemented or not with vitamin D) with PX458-HRC and pcDNA3.1-HRC plasmids and injected mice with lung cancer cells harboring pcDNA3.1-vector or pcDNA3.1-HRC plasmids.
Results: Vitamin D inhibited HRC expression and H460 cell migration and proliferation, and promoted apoptosis compared with controls. The expression of HRC and VDR was significantly upregulated and downregulated, respectively, in lung cancer versus paracancer or normal tissues. Cell proliferation and migration were reduced, apoptotic cells were more and tumors were smaller in mice treated with vitamin D/cholecalciferol cholesterol emulsion (CCE) than in vitamin D/CCE+HRC+/+ mice.
Conclusion: Vitamin D inhibited lung cancer tumor growth, migration, and proliferation by downregulating HRC.
Keywords: Histidine-rich calcium-binding protein; Lung cancer; Vitamin D; Vitamin D receptor.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Cairo University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Maj E., Filip-Psurska B., Milczarek M., Psurski M., Kutner A., Wietrzyk J. Vitamin D derivatives potentiate the anticancer and anti-angiogenic activity of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in combination with cytostatic drugs in an A549 non-small cell lung cancer model. Int J Oncol. 2018;52:337–366. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4228. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Picello E., Damiani E., Margreth A. Low-affinity Ca(2+)-binding sites versus Zn(2+)-binding sites in histidine-rich Ca(2+)-binding protein of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;186:659–667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

