Contemporary outcomes of continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices-a systematic review
- PMID: 33842214
- PMCID: PMC8033255
- DOI: 10.21037/acs-2021-cfmcs-35
Contemporary outcomes of continuous-flow left ventricular assist devices-a systematic review
Abstract
Background: End stage heart failure is a major cause of morbidity and mortality, and its prevalence is expected to rise with the ageing population. For suitable patients, orthotopic heart transplantation remains the gold standard therapy, however, a paucity of donor organs has led to the development of left ventricular assist devices (LVAD). These devices can be utilized as either a bridge-to-transplant (BTT) or as an alternative to heart transplantation. While these devices can prolong life and improve quality of life, they are associated with a significant number of adverse events. We aim to systematically review the literature to quantify survival and the incidence of adverse events following implantation of continuous-flow LVADs (cf-LVAD).
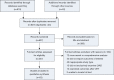
Methods: A systematic review was performed to determine outcomes following implantation of a cf-LVAD. Primary outcomes were survival and frequency of adverse events (such as bleeding, infection, thrombosis, stroke and right ventricular failure). Secondary outcomes included quality of life and assessment of functional status.
Results: Sixty-three studies reported clinical outcomes of 9,280 patients. Survival after cf-LVAD varied between studies. Industry-funded trials generally reported better overall survival than the single- and multi-center case series, which showed significant variation. The largest registry report documented twelve, twenty-four and forty-eight-month survival rates of 82%, 72% and 57% respectively. The most commonly reported adverse events were gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB), device-related infection, neurological events and right heart failure (RHF). Bleeding, RHF and infection were the most frequent complications experienced by those supported with cf-LVAD, occurring in up to 35%, 40% and 55% of patients, respectively. Quality of life as measured using the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) and functional status as measured with the 6-minute walk test (6MWT) improved after cf-LVAD implantation with no decline evident two years after implantation.
Conclusions: The paucity of donor hearts has led to the development of left-ventricular assist devices as a BTT or as a destination therapy (DT). Outcomes after cf-LVAD implantation are excellent, with short-term survival comparable to heart transplantation, but long-term survival remains limited due to the incidence of post-implantation adverse events. Despite these complications, quality of life and functional status improve significantly post-implantation and remain improved over the long-term. This study demonstrates the potential benefits of cf-LVAD therapy whilst also identifying adverse events as an area of increased morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: Left ventricular assist device (LVAD); adverse events; heart failure; survival; systematic review.
2021 Annals of Cardiothoracic Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Lippi G, Sanchis-Gomar F. Global epidemiology and future trends of heart failure. AME Med J 2020;5:15. 10.21037/amj.2020.03.03 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources