The Role of CD276 in Cancers
- PMID: 33842369
- PMCID: PMC8032984
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.654684
The Role of CD276 in Cancers
Abstract
Objective: Aberrant expression of the immune checkpoint molecule, CD276, also known as B7-H3, is associated with tumorigenesis. In this review, we aim to comprehensively describe the role of CD276 in malignancies and its potential therapeutic effect.
Data sources: Database including PubMed, EMbase, Cochrane Library, CNKI, and Clinical Trails.gov were searched for eligible studies and reviews. Study selection: Original studies and review articles on the topic of CD276 in tumors were retrieved.
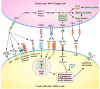
Results: CD276 is an immune checkpoint molecule in the epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) pathway. In this review, we evaluated the available evidence on the expression and regulation of CD276. We also assessed the role of CD276 within the immune micro-environment, effect on tumor progression, and the potential therapeutic effect of CD276 targeted therapy for malignancies.
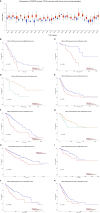
Conclusion: CD276 plays an essential role in cell proliferation, invasion, and migration in malignancies. Results from most recent studies indicate CD276 could be a promising therapeutic target for malignant tumors.
Keywords: B7-H3; CD276; progression; therapeutic target; tumor.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Liang, Liu, Zhang, Wang, Watson, Zhou, Zhang, Wu, Zhang, Lu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

