Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio Is the Independent Prognostic Marker of Progression in Patients Undergoing BCG-Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 33842371
- PMCID: PMC8033152
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.655000
Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio Is the Independent Prognostic Marker of Progression in Patients Undergoing BCG-Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Transurethral resection of bladder tumor with subsequent BCG immunotherapy is the current gold standard in the treatment of high risk and some medium-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Clinical factors like stage, grade, age and gender are well-know predictors of progression to muscle-invasive bladder cancer. In recent years novel hematological biomarkers were shown to be independent predictors of progression. This study aimed to evaluate which of these novel markers has the highest prognostic value of progression in patients with bladder cancer receiving BCG immunotherapy.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed the data of 125 patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer who received BCG immunotherapy. Of these, 61 progressed to muscle-invasive disease or had high-grade recurrence. These patients were compared with the group who did not progress (n = 64). Clinical data including stage, grade, age, gender, smoking status and observational time was collected. Besides, information on blood count analysis was obtained from ambulatory digital charts. On this basis neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR) was counted and compared between groups.
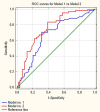
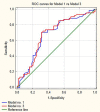
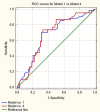
Results: NLR, PLR and LMR were shown to be independent prognostic markers of progression in multivariable analysis. The model with stage, grade, age, gender, smoking status and LMR had the highest prognostic values of all models (area under curve [AUC] = 0.756). The cut-off point according to ROC curves for LMR was 3.25. Adding LMR to the baseline model including clinical variables significantly increased area under curve by 0.08 (p = 0.001). NLR and PLR did not increase areas under curve significantly to baseline model.
Conclusions: LMR outperformed NLR and PLR for prediction of progression in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer receiving BCG immunotherapy. LMR, as an easily obtainable biomarker, should be incorporated to the present risk stratification models.
Keywords: Bacillus Calmet-Guiren immunotherapy; bladder cancer; lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio; transurethral resection of bladder tumor.
Copyright © 2021 Adamkiewicz, Bryniarski, Kowalik, Burzyński, Rajwa and Paradysz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sylvester RJ, Van Der Meijden APM, Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: A combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol (2006) 49(3):466–77. 10.1016/j.eururo.2005.12.031 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

