Draft Genome of Proteus mirabilis Serogroup O18 Elaborating Phosphocholine-Decorated O Antigen
- PMID: 33842384
- PMCID: PMC8027243
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.620010
Draft Genome of Proteus mirabilis Serogroup O18 Elaborating Phosphocholine-Decorated O Antigen
Abstract
Proteus mirabilis is a pathogenic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that causes ascending urinary tract infections. Swarming motility, urease production, biofilm formation, and the properties of its lipopolysaccharide (LPS) are all factors that contribute to the virulence of this bacterium. Uniquely, members of the O18 serogroup elaborate LPS molecules capped with O antigen polymers built of pentasaccharide repeats; these repeats are modified with a phosphocholine (ChoP) moiety attached to the proximal sugar of each O unit. Decoration of the LPS with ChoP is an important surface modification of many pathogenic and commensal bacteria. The presence of ChoP on the bacterial envelope is correlated with pathogenicity, as decoration with ChoP plays a role in bacterial adhesion to mucosal surfaces, resistance to antimicrobial peptides and sensitivity to complement-mediated killing in several species. The genome of P. mirabilis O18 is 3.98 Mb in size, containing 3,762 protein-coding sequences and an overall GC content of 38.7%. Annotation performed using the RAST Annotation Server revealed genes associated with choline phosphorylation, uptake and transfer. Moreover, amino acid sequence alignment of the translated licC gene revealed it to be homologous to LicC from Streptococcus pneumoniae encoding CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase. Recognized homologs are located in the O antigen gene clusters of Proteus species, near the wzx gene encoding the O antigen flippase, which translocates lipid-linked O units across the inner membrane. This study reveals the genes potentially engaged in LPS decoration with ChoP in P. mirabilis O18.
Keywords: Proteus mirabilis; genome; lipopolysaccharide; phosphocholine; urinary tract infection.
Copyright © 2021 Czerwonka, Gmiter and Durlik-Popińska.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

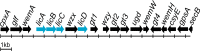
Similar articles
-
Unraveling the genome of Proteus mirabilis strain representing the O78 serogroup: Insights into the unique features of the O-antigen biosynthesis gene cluster.Infect Genet Evol. 2025 Apr;129:105730. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2025.105730. Epub 2025 Feb 23. Infect Genet Evol. 2025. PMID: 39999940
-
Structure and serological characterization of the O-antigen of Proteus mirabilis O18 with a phosphocholine-containing oligosaccharide phosphate repeating unit.Carbohydr Res. 2003 Sep 1;338(18):1835-42. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(03)00274-x. Carbohydr Res. 2003. PMID: 12932366
-
Influence of quorum sensing signal molecules on biofilm formation in Proteus mirabilis O18.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2012 Jan;57(1):53-60. doi: 10.1007/s12223-011-0091-4. Epub 2011 Dec 24. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2012. PMID: 22198843 Free PMC article.
-
Into the understanding the multicellular lifestyle of Proteus mirabilis on solid surfaces.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 2;12:864305. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.864305. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36118021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiella pneumoniae as pathogens capable of causing co-infections and exhibiting similarities in their virulence factors.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Oct 20;12:991657. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.991657. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36339335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The biosynthesis and role of phosphorylcholine in pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria.Trends Microbiol. 2023 Jul;31(7):692-706. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2023.01.006. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Trends Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36863982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphocholine decoration of Proteus mirabilis O18 LPS induces hydrophobicity of the cell surface and electrokinetic potential, but does not alter the adhesion to solid surfaces.Cell Surf. 2022 Jun 15;8:100079. doi: 10.1016/j.tcsw.2022.100079. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cell Surf. 2022. PMID: 35757110 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

