Control Strategies for Carcinogenic-Associated Helminthiases: An Integrated Overview
- PMID: 33842386
- PMCID: PMC8025785
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.626672
Control Strategies for Carcinogenic-Associated Helminthiases: An Integrated Overview
Abstract
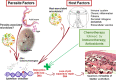
Helminthiases are extremely prevalent in the developing world. In addition, the chronic infection with some parasitic worms are classified as carcinogenic. Therefore, it is utmost importance to understand the parasite-host interactions, the mechanisms underlay carcinogenesis and how they could be counteracted. This knowledge may ultimately guide novel control strategies that include chemotherapy-based approaches targeting these pathogens and associated pathologies caused by their infections. Little is known on how some helminthiases are associated with cancer; however, it has been hypothesized that chemical carcinogenesis may be involved in the process. Here, we summarize the current knowledge on chemical carcinogenesis associated with helminthiases, along with available therapeutic options and potential therapeutic alternatives including chemotherapy and/or immunotherapy. Ideally, the treatment of the carcinogenic helminthiases should target both the parasite and associated pathologies. The success of any chemotherapeutic regimen often depends on the host immune response during the infection and nutritional status among other factors. The close association between chemotherapy and cell-mediated immunity suggests that a dual therapeutic approach would be advantageous. In addition, there is a pressing need for complementary drugs that antagonize the carcinogenesis process associated with the helminth infections.
Keywords: antioxidants; carcinogenesis; chemotherapy; helminths; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2021 da Costa, Gouveia, Rinaldi, Brindley, Santos and Santos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aires A. L., Alburquerque M. C. P. A., Silva R. A., Schirato G. V., de Pontes Filho N. T., de Araújo S. B., et al. (2012). Immunohistopathological changes in murine schistosomiasis mansoni under the influence of N-acetyl-L-cysteine. Parasitol. Res. 111, 1569–1578. 10.1007/s00436-012-2997-4 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

