Aberrantly Expressed Galectin-9 Is Involved in the Immunopathogenesis of Anti-MDA5-Positive Dermatomyositis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease
- PMID: 33842457
- PMCID: PMC8027128
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.628128
Aberrantly Expressed Galectin-9 Is Involved in the Immunopathogenesis of Anti-MDA5-Positive Dermatomyositis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease
Abstract
Background: Dermatomyositis (DM) associated rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (RP-ILD) has high mortality rate and poor prognosis. Galectin-9 (Gal-9) plays multiple functions in immune regulation. We investigated Gal-9 expression in DM patients and its association with DM-ILD.
Methods: A total of 154 idiopathic inflammatory myopathy patients and 30 healthy controls were enrolled in the study. Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies were used to analyze the association between serum Gal-9 levels and clinical features. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and qRT-PCR were used to examine Gal-9 expression in the sera and isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from DM patients. Immunohistochemistry was performed to analyze the expression of Gal-9 and its ligand (T-cell immunoglobulin mucin (Tim)-3 and CD44) in lung tissues from anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5)-positive patients. The effect of Gal-9 on human lung fibroblasts (MRC-5) was investigated in vitro.
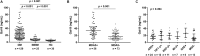
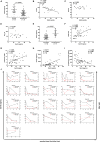
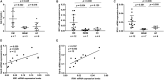
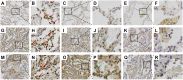
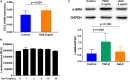
Results: Serum Gal-9 levels were significantly higher in DM patients than in immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy patients and healthy controls (all p < 0.001). Higher serum Gal-9 levels were observed in anti-MDA5-positive DM patients than in anti-MDA5-negative DM patients [33.8 (21.9-44.7) vs. 16.2 (10.0-26.9) ng/mL, p < 0.001]. Among the anti-MDA5-positive DM patients, serum Gal-9 levels were associated with RP-ILD severity. Serum Gal-9 levels were significantly correlated with disease activity in anti-MDA5-positive DM patients in both cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. PBMCs isolated from anti-MDA5-positive DM patients (3.7 ± 2.3 ng/mL) produced higher levels of Gal-9 than those from immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy patients (1.1 ± 0.3 ng/mL, p = 0.022) and healthy controls (1.4 ± 1.2 ng/mL, p = 0.045). The mRNA levels of Gal-9 were positively correlated with the levels of type-I interferon-inducible genes MX1 (r = 0.659, p = 0.020) and IFIH1 (r = 0.787, p = 0.002) in PBMCs from anti-MDA5-positive DM patients. Immunohistochemistry revealed increased Gal-9 and Tim-3 expression in the lung tissues of patients with DM and RP-ILD. In vitro stimulation with Gal-9 protein increased CCL2 mRNA expression in MRC-5 fibroblasts.
Conclusions: Among anti-MDA5-positive DM patients, Gal-9 could be a promising biomarker for monitoring disease activity, particularly for RP-ILD severity. Aberrant expression of the Gal-9/Tim-3 axis may be involved in the immunopathogenesis of DM-ILD.
Keywords: biomarker; dermatomyositis; galectin-9; interstitial lung disease; melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5.
Copyright © 2021 Liang, Zhang, Shen, Song, Li, Ye, Lu, Wang and Peng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated serum B-cell activator factor levels predict rapid progressive interstitial lung disease in anti-melanoma differentiation associated protein 5 antibody positive dermatomyositis.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Apr 19;19(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03153-6. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 38637830 Free PMC article.
-
Different Multivariable Risk Factors for Rapid Progressive Interstitial Lung Disease in Anti-MDA5 Positive Dermatomyositis and Anti-Synthetase Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 7;13:845988. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.845988. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35320936 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated CD38 expression on T cells was associated with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 positive dermatomyositis.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 11;15:1455944. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1455944. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39588376 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of biomarkers in anti-MDA5-positive dermatomyositis, associated interstitial lung disease, and rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Nov;36(11):e24726. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24726. Epub 2022 Oct 12. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 36221983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical spectrum and therapeutics in Canadian patients with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5)-positive dermatomyositis: a case-based review.Rheumatol Int. 2019 Nov;39(11):1971-1981. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04398-2. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Rheumatol Int. 2019. PMID: 31375890 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of monocytes and macrophages in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: insights into pathogenesis and potential targets.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 20;16:1567833. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1567833. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40181992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti- Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Gene 5 Antibody Positive Dermatomyositis: Recent Progress in Pathophysiology and Treatment.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2025 May 5;27(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s11926-025-01188-7. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40323493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genetics of Autoimmune Myositis.Front Immunol. 2022 May 26;13:886290. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.886290. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35693792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of poor prognosis of dermatomyositis and clinical value of ferritin/Kl-6 in predicting prognosis.Skin Res Technol. 2024 May;30(5):e13701. doi: 10.1111/srt.13701. Skin Res Technol. 2024. PMID: 38682785 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Exploring efficacy of tofacitinib in modulating interferon response in five case of anti-MDA5+ dermatomyositis with interstitial lung disease.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 4;16:1515602. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1515602. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39967677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellutti Enders F., van Wijk F., Scholman R., Hofer M., Prakken B. J., van Royen-Kerkhof A., et al. (2014). Correlation of CXCL10, tumor necrosis factor receptor type II, and galectin 9 with disease activity in juvenile dermatomyositis. Arthrit. Rheumatol. 66 2281–2289. 10.1002/art.38676 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

