Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology and Current Treatments, to Future Agents
- PMID: 33842503
- PMCID: PMC8032930
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.642296
Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology and Current Treatments, to Future Agents
Abstract
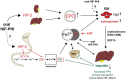
Anemia is a common complication in chronic kidney disease (CKD), and is associated with a reduced quality of life, and an increased morbidity and mortality. The mechanisms involved in anemia associated to CKD are diverse and complex. They include a decrease in endogenous erythropoietin (EPO) production, absolute and/or functional iron deficiency, and inflammation with increased hepcidin levels, among others. Patients are most commonly managed with oral or intravenous iron supplements and with erythropoiesis stimulating agents (ESA). However, these treatments have associated risks, and sometimes are insufficiently effective. Nonetheless, in the last years, there have been some remarkable advances in the treatment of CKD-related anemia, which have raised great expectations. On the one hand, a novel family of drugs has been developed: the hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors (HIF-PHIs). These agents induce, among other effects, an increase in the production of endogenous EPO, improve iron availability and reduce hepcidin levels. Some of them have already received marketing authorization. On the other hand, recent clinical trials have elucidated important aspects of iron supplementation, which may change the treatment targets in the future. This article reviews the current knowledge of the pathophysiology CKD-related anemia, current and future therapies, the trends in patient management and the unmet goals.
Keywords: COVID 19; HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor; HIF stabilizer; anemia; chronic kidney disease; erythropoiesis-stimulating agents; hepcidin; iron.
Copyright © 2021 Portolés, Martín, Broseta and Cases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

