Omecamtiv mecarbil evokes diastolic dysfunction and leads to periodic electromechanical alternans
- PMID: 33844095
- PMCID: PMC8041714
- DOI: 10.1007/s00395-021-00866-8
Omecamtiv mecarbil evokes diastolic dysfunction and leads to periodic electromechanical alternans
Abstract
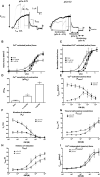
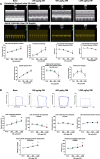
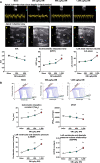
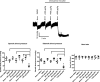
Omecamtiv mecarbil (OM) is a promising novel drug for improving cardiac contractility. We tested the therapeutic range of OM and identified previously unrecognized side effects. The Ca2+ sensitivity of isometric force production (pCa50) and force at low Ca2+ levels increased with OM concentration in human permeabilized cardiomyocytes. OM (1 µM) slowed the kinetics of contractions and relaxations and evoked an oscillation between normal and reduced intracellular Ca2+ transients, action potential lengths and contractions in isolated canine cardiomyocytes. Echocardiographic studies and left ventricular pressure-volume analyses demonstrated concentration-dependent improvements in cardiac systolic function at OM concentrations of 600-1200 µg/kg in rats. Administration of OM at a concentration of 1200 µg/kg was associated with hypotension, while doses of 600-1200 µg/kg were associated with the following aspects of diastolic dysfunction: decreases in E/A ratio and the maximal rate of diastolic pressure decrement (dP/dtmin) and increases in isovolumic relaxation time, left atrial diameter, the isovolumic relaxation constant Tau, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and the slope of the end-diastolic pressure-volume relationship. Moreover, OM 1200 µg/kg frequently evoked transient electromechanical alternans in the rat in vivo in which normal systoles were followed by smaller contractions (and T-wave amplitudes) without major differences on the QRS complexes. Besides improving systolic function, OM evoked diastolic dysfunction and pulsus alternans. The narrow therapeutic window for OM may necessitate the monitoring of additional clinical safety parameters in clinical application.
Keywords: Ca2+ sensitivity; Diastolic dysfunction; Heart failure; Inotropy; Omecamtiv mecarbil; Pulsus alternans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures
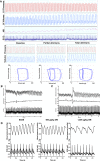

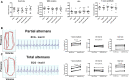

References
-
- Bakkehaug JP, Kildal AB, Engstad ET, Boardman N, Naesheim T, Ronning L, Aasum E, Larsen TS, Myrmel T, How OJ. Myosin activator omecamtiv mecarbil increases myocardial oxygen consumption and impairs cardiac efficiency mediated by resting myosin ATPase activity. Circ Heart Fail. 2015;8:766–775. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.114.002152. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cleland JG, Teerlink JR, Senior R, Nifontov EM, Mc Murray JJ, Lang CC, Tsyrlin VA, Greenberg BH, Mayet J, Francis DP, Shaburishvili T, Monaghan M, Saltzberg M, Neyses L, Wasserman SM, Lee JH, Saikali KG, Clarke CP, Goldman JH, Wolff AA, Malik FI. The effects of the cardiac myosin activator, omecamtiv mecarbil, on cardiac function in systolic heart failure: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover, dose-ranging phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2011;378:676–683. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61126-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Greenberg BH, Chou W, Saikali KG, Escandon R, Lee JH, Chen MM, Treshkur T, Megreladze I, Wasserman SM, Eisenberg P, Malik FI, Wolff AA, Shaburishvili T. Safety and tolerability of omecamtiv mecarbil during exercise in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and angina. JACC Heart Fail. 2015;3:22–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2014.07.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GINOP-2.3.2-15-2016-00043/Ministry for National Economy of Hungary, co-financed by the European Union and the European Regional Development Fund
- ÚNKP-18-3-III-DE-209/Ministry of Human Capacities of Hungary, co-financed by the European Union and the European Regional Development Fund
- ED_18-1-2019-0028, TKP2020-IKA-04 and TKP2020-NKA-04/The Thematic Excellence Programme of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology, also supported from the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary
- FK 128809/National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary
- FK 128116/National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary
- K 134939/National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary.
- K 116940 and K 132623/National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary.
- Therapeutic Development thematic programme of the Semmelweis University/Higher Education Institutional Excellence Programme of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology in Hungary
- 2020-4.1.1.-TKP2020, Therapeutic Development and Bioimaging thematic programme of the Semmelweis University/The Thematic Excellence Programme of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology was also supported from the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund of Hungary
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

