Impact of moderate exercise on fatty acid oxidation in pancreatic β-cells and skeletal muscle
- PMID: 33844166
- PMCID: PMC8357749
- DOI: 10.1007/s40618-021-01551-2
Impact of moderate exercise on fatty acid oxidation in pancreatic β-cells and skeletal muscle
Abstract
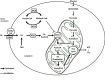
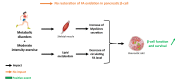
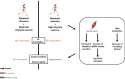
Fatty acids (FA) play a crucial role in glycaemia regulation in healthy and metabolic disorders conditions through various mechanisms. FA oxidation is one of the processes involved in lipid metabolism and can be modulated by exercise. Nowadays, physical activity is known to be an effective strategy for the prevention and treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Moreover, its intensity, its duration, the sex-gender, the prandial state, exerkines… are as many parameters that can influence glycaemic control. However, the widely debated question is to determine the best type of exercise for patients with metabolic disorders. In this review, we will discuss the impact of exercise intensity, especially moderate activity, on glycaemic control by focussing on FA oxidation in pancreatic β-cells and skeletal muscle. Finally, thanks to all the recent data, we will determine whether moderate physical activity is a good therapeutic strategy and if FA oxidation represents a target of interest to treat diabetic, obese and insulin-resistant patients.
Keywords: FA oxidation; Moderate exercise; Pancreatic beta cell; Skeletal muscle.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lupi R, et al. Prolonged exposure to free fatty acids has cytostatic and pro-apoptotic effects on human pancreatic islets: evidence that beta-cell death is caspase mediated, partially dependent on ceramide pathway, and Bcl-2 regulated. Diabetes. 2002;51(5):1437–1442. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.5.1437. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

