The High Affinity Dopamine D2 Receptor Agonist MCL-536: A New Tool for Studying Dopaminergic Contribution to Neurological Disorders
- PMID: 33844498
- PMCID: PMC8426090
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00094
The High Affinity Dopamine D2 Receptor Agonist MCL-536: A New Tool for Studying Dopaminergic Contribution to Neurological Disorders
Abstract
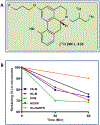
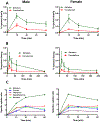
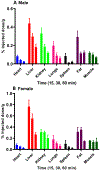
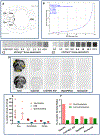
The dopamine D2 receptor exists in two different states, D2high and D2low; the former is the functional form of the D2 receptor and associates with intracellular G-proteins. The D2 agonist [3H]MCL-536 has high affinity for the D2 receptor (Kd 0.8 nM) and potently displaces the binding of (R-(-)-N-n-propylnorapomorphine (NPA; Ki 0.16 nM) and raclopride (Ki 0.9 nM) in competition binding assays. Here, we further characterize [3H]MCL-536. [3H]MCL-536 was metabolically stable, with about 75% of the compound remaining intact after 1 h incubation with human liver microsomes. Blood-brain barrier penetration in rats was good, attaining at 15 min a % injected dose per gram of wet tissue (%ID/g) of 0.28 in males versus 0.42 in females in the striatum. Specific uptake ratios ([%ID/g striatum]/[%ID/g cerebellum]) were stable in males during the first 60 min and in females up to 15-30 min. The D2-rich striatum exhibited the highest uptake and slowest washout compared to D2-poor cortex or cerebellum. In peripheral organs, uptake peaked at 15 min but declined to baseline at 60 min, indicating good clearance from the body. In vitro autoradiography on transaxial and coronal brain sections showed specific binding of [3H]MCL-536, which was abolished by preincubation with D2/D3 ligands sulpiride, NPA, and raclopride and in the presence of the stable GTP analogue guanylylimidodiphosphate. In amphetamine-sensitized animals, striatal binding was higher than in controls, indicating specificity for the D2high receptor state. [3H]MCL-536's unique properties make it a valuable tool for research on neurological disorders involving the dopaminergic system like Parkinson's disease or schizophrenia.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; aporphine; dopamine D2high receptor; schizophrenia; tritiated radioligand.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New Dopamine D2 Receptor Agonist, [3H]MCL-536, for Detecting Dopamine D2high Receptors in Vivo.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Jun 20;9(6):1283-1289. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00096. Epub 2018 Apr 16. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29641175 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine agonist radioligand binds to both D2High and D2Low receptors, explaining why alterations in D2High are not detected in human brain scans.Synapse. 2012 Jan;66(1):88-93. doi: 10.1002/syn.20987. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Synapse. 2012. PMID: 21954082
-
Dopamine D2High receptors measured ex vivo are elevated in amphetamine-sensitized animals.Synapse. 2009 Mar;63(3):186-92. doi: 10.1002/syn.20595. Synapse. 2009. PMID: 19086090
-
N-(4-(4-(2-(2-[18F]Fluoroethoxy)phenyl)piperazine-1-yl)butyl)-4-(3-thienyl)benzamide.2011 Jun 24 [updated 2011 Oct 6]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 Jun 24 [updated 2011 Oct 6]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 21994970 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
(R)-(-)-2-Chloro-N-[1-11C-propyl]n-propylnorapomorphine.2010 Oct 24 [updated 2010 Dec 11]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2010 Oct 24 [updated 2010 Dec 11]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 21204317 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Product-Inspired Dopamine Receptor Ligands.J Med Chem. 2024 Aug 8;67(15):12463-12484. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00537. Epub 2024 Jul 22. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39038276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
History of the dopamine hypothesis of antipsychotic action.World J Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 19;11(7):355-364. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i7.355. eCollection 2021 Jul 19. World J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34327128 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bozzi Y, and Borrelli E (2006) Dopamine in neurotoxicity and neuroprotection: what do D2 receptors have to do with it? Trends Neurosci. 29 (3), 167–74. - PubMed
-
- Corripio I, Escarti MJ, Portella MJ, Perez V, Grasa E, Sauras RB, Alonso A, Safont G, Camacho MV, Duenas R, Arranz B, et al. (2011) Density of striatal D2 receptors in untreated first-episode psychosis: an I123-IBZM SPECT study. Eur. Neuro-psychopharmacol 21 (12), 861–6. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman JA, Kane JM, and Alvir J (1987) Provocative tests with psychostimulant drugs in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 91 (4), 415–33. - PubMed
-
- Seeman P (2008) Dopamine D2(High) receptors on intact cells. Synapse 62 (4), 314–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

