Immunogenicity and safety of a nine-valent human papillomavirus vaccine in Vietnamese males and females (9 to 26 years of age): an open-label, phase 3 trial
- PMID: 33844623
- PMCID: PMC8189095
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1865739
Immunogenicity and safety of a nine-valent human papillomavirus vaccine in Vietnamese males and females (9 to 26 years of age): an open-label, phase 3 trial
Abstract
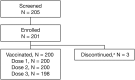
This open-label, single-center, Phase 3 study (NCT03546842) assessed the immunogenicity and safety of the nine-valent human papillomavirus (9vHPV; HPV6/11/16/18/31/33/45/52/58) vaccine in Vietnamese males and females, with the aim to support 9vHPV vaccine licensure in Vietnam. Participants aged 9-26 years received three 9vHPV vaccine doses (Day 1, Month 2, Month 6). Serum samples were obtained on Day 1 (pre-vaccination) and at Month 7 (one month post-Dose 3) for the measurement of anti-HPV antibodies. Geometric mean titers (GMTs) and seroconversion percentages were obtained using the HPV-9 competitive Luminex immunoassay. Injection-site adverse events (AEs), systemic AEs, serious AEs (SAEs), and study discontinuations due to AEs were recorded. Of 201 participants enrolled, 200 (99.5%) received ≥1 vaccine dose. All participants who received the three-dose regimen (198/200, 98.5%) seroconverted for all 9vHPV vaccine types by Month 7. Robust anti-HPV GMT responses were also observed. Half of participants (50.5%) reported ≥1 AE; the majority were injection-site-related (45.0%) and mild (43.0%). There were no deaths, vaccine-related SAEs, or discontinuations due to AEs. Administration of three 9vHPV vaccine doses was highly immunogenic and resulted in acceptable seropositivity percentages for all vaccine HPV types. The 9vHPV vaccine was generally well tolerated among this study population.Region of origin: VietnamTrial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier NCT03546842.
Keywords: Human papillomavirus (HPV); Vietnam; immunogenicity; nine-valent human papillomavirus vaccine; safety.
Figures
References
-
- Bruni L, Albero G, Serrano B, Mena M, Gómez D, Muñoz J, Bosch FX, de Sanjosé S. ICO/IARC Information Centre on HPV and Cancer (HPV Information Centre). Human Papillomavirus and Related Diseases in Vietnam. Summary Report. 2019. [accessed 2020 June30]. https://hpvcentre.net/statistics/reports/VNM.pdf
-
- Bergman H, Buckley BS, Villanueva G, Petkovic J, Garritty C, Lutje V, Riveros-Balta AX, Low N, Henschke N. Comparison of different human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine types and dose schedules for prevention of HPV‐related disease in females and males. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;2019(11):CD013479. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013479. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
