Screening Tools Based on Nomogram for Diabetic Kidney Diseases in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- PMID: 33844903
- PMCID: PMC8497917
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0117
Screening Tools Based on Nomogram for Diabetic Kidney Diseases in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Abstract
Background: The influencing factors of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were explored to develop and validate a DKD diagnostic tool based on nomogram approach for patients with T2DM.
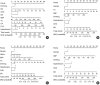
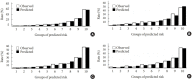
Methods: A total of 2,163 in-hospital patients with diabetes diagnosed from March 2015 to March 2017 were enrolled. Specified logistic regression models were used to screen the factors and establish four different diagnostic tools based on nomogram according to the final included variables. Discrimination and calibration were used to assess the performance of screening tools.
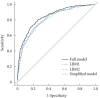
Results: Among the 2,163 participants with diabetes (1,227 men and 949 women), 313 patients (194 men and 120 women) were diagnosed with DKD. Four different screening equations (full model, laboratory-based model 1 [LBM1], laboratory-based model 2 [LBM2], and simplified model) showed good discriminations and calibrations. The C-indexes were 0.8450 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.8202 to 0.8690) for full model, 0.8149 (95% CI, 0.7892 to 0.8405) for LBM1, 0.8171 (95% CI, 0.7912 to 0.8430) for LBM2, and 0.8083 (95% CI, 0.7824 to 0.8342) for simplified model. According to Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test, good agreement between the predicted and observed DKD events in patients with diabetes was observed for full model (χ2=3.2756, P=0.9159), LBM1 (χ2=7.749, P=0.4584), LBM2 (χ2=10.023, P=0.2634), and simplified model (χ2=12.294, P=0.1387).
Conclusion: LBM1, LBM2, and simplified model exhibited excellent predictive performance and availability and could be recommended for screening DKD cases among Chinese patients with diabetes.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Diabetic nephropathies; Nomograms; Risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developing screening tools to estimate the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Technol Health Care. 2024;32(3):1807-1818. doi: 10.3233/THC-230811. Technol Health Care. 2024. PMID: 37980579
-
Development and validation of a novel nomogram to predict diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetic mellitus and proteinuric kidney disease.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Jan;55(1):191-200. doi: 10.1007/s11255-022-03299-x. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 35870041
-
Nomogram to predict the risk of acute kidney injury in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: an analysis of the MIMIC-III database.BMC Endocr Disord. 2021 Mar 4;21(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00696-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021. PMID: 33663489 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Validation of a Risk Prediction Model for Early Diabetic Kidney Disease Based on a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 20 Cohorts.Diabetes Care. 2020 Apr;43(4):925-933. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1897. Diabetes Care. 2020. PMID: 32198286
-
Clinical predictive factors in diabetic kidney disease progression.J Diabetes Investig. 2017 Jan;8(1):6-18. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12533. Epub 2016 Jun 8. J Diabetes Investig. 2017. PMID: 27181363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nomogram-Based Chronic Kidney Disease Prediction Model for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Using Routine Pathological Data.J Pers Med. 2022 Sep 14;12(9):1507. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091507. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36143293 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Serum Lactate Level-Based Nomograms for Predicting Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Mar 1;17:1051-1068. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S453543. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 38445169 Free PMC article.
-
Risk prediction models for diabetic nephropathy among type 2 diabetes patients in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 3;15:1407348. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1407348. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39022345 Free PMC article.
-
Development and assessment of diabetic nephropathy prediction model using hub genes identified by weighted correlation network analysis.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Oct 14;14(19):8095-8109. doi: 10.18632/aging.204340. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 36242604 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Dimensional Ultrasound-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Pilot Study.Int J Gen Med. 2024 May 6;17:1877-1885. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S462896. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 38736665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis G, Maxwell AP. Risk factor control is key in diabetic nephropathy. Practitioner. 2014;258:13–7. - PubMed
-
- KDOQI Guideline 2: management of hyperglycemia and general diabetes care in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;49(2 Suppl 2):S62–73.
-
- World Health Organization . Geneva: WHO; 2016. WHO Global report on diabetes.
-
- Quan J, Li TK, Pang H, Choi CH, Siu SC, Tang SY, et al. Diabetes incidence and prevalence in Hong Kong, China during 2006-2014. Diabet Med. 2017;34:902–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

