CT Radiomic Features for Predicting Resectability and TNM Staging in Thymic Epithelial Tumors
- PMID: 33844992
- PMCID: PMC9475805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2021.03.084
CT Radiomic Features for Predicting Resectability and TNM Staging in Thymic Epithelial Tumors
Abstract
Background: To explore the performance of a computed tomography based radiomics model in the preoperative prediction of resectability status and TNM staging in thymic epithelial tumors.
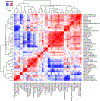
Methods: We reviewed the last preoperative computed tomography scan of patients with thymic epithelial tumors prior to resection and pathology evaluation at our institution between February 2008 and June 2019. A total of 101 quantitative features were extracted and a radiomics model was trained using elastic net penalized logistic regressions for each aim. In the set-aside testing sets, discriminating performance of each model was assessed with area under receiver operating characteristic curve.
Results: Our final population consisted of 243 patients with: 153 (87%) thymomas, 23 (9%) thymic carcinomas, and 9 (4%) thymic carcinoids. Incomplete resections (R1 or R2) occurred in 38 (16%) patients, and 67 (28%) patients had more advanced stage tumors (stage III or IV). In the set-aside testing sets, the radiomics model achieved good performance in preoperatively predicting incomplete resections (area under receiver operating characteristic curve: 0.80) and advanced stage tumors (area under receiver operating characteristic curve: 0.70).
Conclusions: Our computed tomography radiomics model achieved good performance to predict resectability status and staging in thymic epithelial tumors, suggesting a potential value for the evaluation of radiomic features in the preoperative prediction of surgical outcomes in thymic malignancies.
Copyright © 2022 The Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


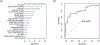

References
-
- Regnard J-F, Magdeleinat P, Dromer C, et al. Prognostic factors and long-term results after thymoma resection: A series of 307 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996;112(2):376–384. - PubMed
-
- Kondo K, Monden Y. Therapy for thymic epithelial tumors: a clinical study of 1,320 patients from Japan. The Annals of thoracic surgery. 2003;76(3):878–884; discussion 884–875. - PubMed
-
- Lardinois D, Rechsteiner R, Läng RH, et al. Prognostic relevance of Masaoka and Müller-Hermelink classification in patients with thymic tumors. The Annals of thoracic surgery. 2000;69(5):1550–1555. - PubMed
-
- Cardillo G, Carleo F, Giunti R, et al. Predictors of survival in patients with locally advanced thymoma and thymic carcinoma (Masaoka stages III and IVa). Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010;37(4):819–823. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

