Tremelimumab plus durvalumab retreatment and 4-year outcomes in patients with mesothelioma: a follow-up of the open label, non-randomised, phase 2 NIBIT-MESO-1 study
- PMID: 33844995
- PMCID: PMC9765708
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00043-6
Tremelimumab plus durvalumab retreatment and 4-year outcomes in patients with mesothelioma: a follow-up of the open label, non-randomised, phase 2 NIBIT-MESO-1 study
Abstract
Background: The NIBIT-MESO-1 study demonstrated the efficacy and safety of tremelimumab combined with durvalumab in patient with unresectable mesothelioma followed up for a median of 52 months [IQR 49-53]. Here, we report 4-year survival and outcomes after retreatment, and the role of tumour mutational burden (TMB) in identifying patients who might have a better outcome in response to combined therapy.
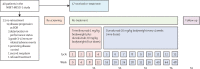
Methods: NIBIT-MESO-1 was an open-label, non-randomised, phase 2 trial of patients with unresectable pleural or peritoneal mesothelioma who received intravenous tremelimumab (1 mg/kg bodyweight) and durvalumab (20 mg/kg bodyweight) every 4 weeks for four doses, followed by maintenance intravenous durvalumab at the same dose and schedule for nine doses. In this follow-up study, patients with disease progression following initial clinical benefit-ie, a partial repsonse or stable disease-were eligible for retreatment and with the same doses and schedules for tremelimumab and durvalumab as used in the NIBIT-MESO-1 trial. The primary endpoint, immune-related objective response rate, was evaluated per immune-related modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) or immune-related RECIST 1.1 criteria for patients with pleural or peritoneal malignant mesothelioma, respectively. Key secondary endpoints were overall survival and safety, and TMB was also evaluated post hoc in patients who had tumour tissue available before treatment. The intention-to-treat population was used for analysis of all efficacy endpoints. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT02588131.
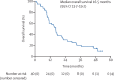
Findings: 40 patients were enrolled in the NIBIT-MESO-1 study between Oct 30, 2015, and Oct 12, 2016. At data cut-off, April 30, 2020, five (13%) of 40 patients were alive, and 35 (88%) patients had died of progressive disease. At a median follow-up of 52 months (IQR 49-53), median overall survival was 16·5 months (95% CI 13·7-19·2). Survival was 20% (eight of 40 patients) at 36 months and 15% (six of 40 patients) and 48 months. 17 (43%) of 40 patients met the criteria for enrolment in the retreatment study and were retreated with at least one dose of tremelimumab and durvalumab. No immune-related objective responses were observed in the 17 retreated patients. Seven (41%) of 17 patients achieved immune-related stable disease. From the start of retreatment to a median follow-up of 24 months (22·0-25·0), median overall survival was 12·5 months (95% CI 0·0-25·8), and survival at 12 months was 52·9%, at 18 months was 35·3%, and at 24 months was 23·5%. There were no grade 3-4 immune-related adverse events in the retreatment cohort. In a post-hoc analysis of 28 patients for whom tumour tissue before treatment was available, patients with a TMB higher than the median value of 8·3 mutations per Mb had a higher median overall survival compared with patients with TMB below the median value, but this difference was non-significant. Moreover, when patients were additionally stratified for ICI retreatment (n=13), there was a significant difference in survival between those with a TMB higher than the median of 8·3 mutations per Mb and those with TMB lower than the median in the retreated cohort (41·3 months vs 17·4 months; p=0·02).
Interpretation: Tremelimumab combined with durvalumab was associated with long-term survival in patients with mesothelioma. Retreatment was safe and resulted in clinically meaningful outcomes, thus suggesting its potential application in the clinical practice of mesothalioma patients.
Funding: NIBIT Foundation, Fondazione AIRC, AstraZeneca.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests LC has served as consultant or advisor to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, and Merck Sharp & Dohme, and received compensated educational activities from Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, and Sanofi. AMDG has served as a consultant or advisor to Incyte, Pierre Fabre, GlaxoSmith Kline, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Sanofi. MM has served as a consultant or advisor to Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Incyte, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Pierre Fabre, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmith Kline, Sciclone, Sanofi, Alfasigma, and Merck Serono. MM and AC own shares in Epigen Therapeutics. GP currently has or has previously had an advisory role for Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, and Roche–Genentech. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment on
-
COVID-19 severity and obesity: are MAIT cells a factor?Lancet Respir Med. 2021 May;9(5):445-447. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00140-5. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 33844997 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vogelzang NJ, Rusthoven JJ, Symanowski J, et al. Phase 3 study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2636–2644. - PubMed
-
- Zalcman G, Mazieres J, Margery J, et al. Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the Mesothelioma Avastin Cisplatin Pemetrexed Study (MAPS): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1405–1414. - PubMed
-
- Buikhuisen WA, Hiddinga BI, Baas P, van Meerbeeck JP. Second line therapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review. Lung Cancer. 2015;89:223–231. - PubMed
-
- Calabrò L, Morra A, Fonsatti E, et al. Tremelimumab for patients with chemotherapy-resistant advanced malignant mesothelioma: an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:1104–1111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

