Renal and cardiovascular repercussions in preeclampsia and their impact on fluid management: a literature review
- PMID: 33845102
- PMCID: PMC9373504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjane.2021.02.052
Renal and cardiovascular repercussions in preeclampsia and their impact on fluid management: a literature review
Abstract
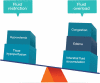
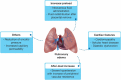
Preeclampsia is a multifactorial condition associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Fluid therapy in these patients is challenging since volume expansion may precipitate pulmonary edema, and fluid restriction may worsen renal function. Furthermore, cardiac impairment may introduce an additional component to the hemodynamic management. This article reviews the repercussions of preeclampsia on renal and cardiovascular systems and the development of pulmonary edema, as well as to discuss fluid management, focusing on the mitigation of adverse outcomes and monitoring alternatives. The literature review was carried out using PubMed, Embase, and Google Scholar databases from May 2019 to March 2020. Papers addressing the subjects of interest were included regardless of the publication language. There is a current trend towards restricting the administration of fluids in women with non-complicated preeclampsia. However, patients with preeclampsia may experience hemorrhagic shock, requiring volume resuscitation. In this case, hemodynamic monitoring is recommended to guide fluid therapy while avoiding complications.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Cardiovascular; Fluid management; Preeclampsia; Pulmonary edema; Review article.
Copyright © 2021 Sociedade Brasileira de Anestesiologia. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of lung and cardiac ultrasound for cardiovascular hemodynamic assessment of women with preeclampsia.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2024 Mar;6(3):101306. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2024.101306. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2024. PMID: 38301997 Review.
-
Preeclampsia: an update.Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2014;65(4):137-49. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2014. PMID: 25622379 Review.
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in preeclampsia complicated by pulmonary edema shows myocardial edema with normal left ventricular systolic function.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Aug;227(2):292.e1-292.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2022.03.009. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 35283087
-
The impact of the definition of preeclampsia on disease diagnosis and outcomes: a retrospective cohort study.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Feb;224(2):217.e1-217.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.08.019. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 32795430
-
Fluid and volume monitoring.Int J Artif Organs. 2008 Feb;31(2):111-26. doi: 10.1177/039139880803100205. Int J Artif Organs. 2008. PMID: 18311728
Cited by
-
The Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Pattern of Dyslipidemia Associated with Iodine Deficiency and Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Pregnant Normotensive and Preeclamptic Central African Women.Pathophysiology. 2025 Apr 18;32(2):18. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology32020018. Pathophysiology. 2025. PMID: 40265443 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Plasma Calorimetric Profiles of Women with Preeclampsia: Effect of Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 29;12(5):1032. doi: 10.3390/antiox12051032. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237898 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Eclampsia.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Aug 23;11(9):257. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11090257. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 39330315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rare case with double trouble: Peripartum cardiomyopathy and preeclampsia together with placental abruption resulting in both cardiac and kidney failure.J Family Med Prim Care. 2024 Jul;13(7):2789-2791. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1469_23. Epub 2024 Jun 28. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 39071004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 202 Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133:e1–e25. - PubMed
-
- Abalos E., Cuesta C., Grosso A.L., et al. Global and regional estimates of preeclampsia and eclampsia: a systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013;170:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Vigil-De Gracia P. Maternal deaths due to eclampsia and HELLP syndrome. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2009;104:90–94. - PubMed
-
- Hutcheon J.A., Lisonkova S., Joseph K.S. Epidemiology of pre-eclampsia and the other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;25:391–403. - PubMed
-
- Roberts JM, Redman CW. Pre-eclampsia: more than pregnancy-induced hypertension. Lancet. 1993;341:1447–1451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources