Factors Affecting Dilation Interval in Patients With Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis-Associated Subglottic and Glottic Stenosis
- PMID: 33845664
- PMCID: PMC8511351
- DOI: 10.1177/01945998211004264
Factors Affecting Dilation Interval in Patients With Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis-Associated Subglottic and Glottic Stenosis
Abstract
Objective: Subglottic stenosis (SGS) is a known complication of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA). We investigated the impact of medical and surgical interventions on the surgical dilation interval and characterized patients with glottic involvement.
Study design: A retrospective chart review of patients with GPA-associated SGS was performed from 2010 to 2019.
Setting: Tertiary academic medical center.
Methods: The impact of medical and surgical interventions on dilation interval was assessed. The prevalence of glottic involvement was assessed, and clinical characteristics and outcomes were compared with patients without glottic involvement.
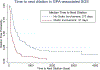
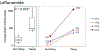
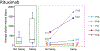
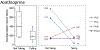
Results: A total of 39 patients with GPA-associated SGS were analyzed. Dilation intervals in patients receiving leflunomide (n = 4; median, 484 days; 95% CI, 405-1099) were greater than in those not receiving leflunomide (median, 155 days; 95% CI, 48-305; P = .033). The surgical technique used did not affect dilation interval. Patients with glottic involvement (n = 13) had a greater incidence of dysphonia (13/13 vs 15/26 [58%], P = .007) and a shorter dilation interval with involvement (median, 91 days; interquartile range, 70-277) versus without involvement (median, 377 days; interquartile range, 175-1148; hazard ratio, 3.38; 95% CI, 2.26-5.05; P < .001). Of 13 patients, 8 (62%) did not have glottic involvement on first presentation.
Conclusion: Although GPA is classically thought to affect the subglottis, it also involves the glottis in a subset of patients. These patients have greater complaints of dysphonia and require more frequent surgery. Systemic therapy may increase dilation intervals. In this preliminary study, patients taking leflunomide demonstrated an improvement, highlighting the need for further study of immunosuppression regimens in the treatment of GPA-associated SGS.
Keywords: dysphonia; glottic stenosis; granulomatosis with polyangiitis; laryngotracheal stenosis; subglottic stenosis; vasculitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical manifestations and treatment of idiopathic and Wegener granulomatosis-associated subglottic stenosis.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 Jan;139(1):76-81. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2013.1135. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013. PMID: 23329095
-
Role of systemic immunosuppression on subglottic stenosis in granulomatosis with polyangiitis: Analysis of a single-centre cohort.Eur J Intern Med. 2023 Aug;114:108-112. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2023.05.006. Epub 2023 May 6. Eur J Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37156712
-
Medical Maintenance Therapy Following Laser Excision in Patients With Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis (GPA)-Associated Subglottic Stenosis.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Jul;171(1):180-187. doi: 10.1002/ohn.694. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 38482973
-
The presentation and management of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's Granulomatosis) in the pediatric airway.Laryngoscope. 2017 Jan;127(1):233-240. doi: 10.1002/lary.26013. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Laryngoscope. 2017. PMID: 27113905 Review.
-
Clinical features and therapeutic management of subglottic stenosis in patients with Wegener's granulomatosis.Lupus. 2008 Sep;17(9):832-6. doi: 10.1177/0961203308089693. Lupus. 2008. PMID: 18755865 Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic and Local Medical or Surgical Therapies for Ear, Nose and/or Throat Manifestations in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Systematic Literature Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 28;12(9):3173. doi: 10.3390/jcm12093173. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37176613 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lutalo PMK, D’Cruz DP. Diagnosis and classification of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (aka Wegener’s granulomatosis). J Autoimmun. 2014;48–49:94–98. - PubMed
-
- Taylor SC, Clayburgh DR, Rosenbaum JT, Schindler JS. Progression and management of Wegener’s granulomatosis in the head and neck. Laryngoscope. 2012;122(8):1695–1700. - PubMed
-
- Martinez Del Pero M, Jayne D, Chaudhry A, Sivasothy P, Jani P. Long-term outcome of airway stenosis in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis): an observational study. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;140(11):1038–1044. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

