Imaging manifestations of Caroli disease with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 33845788
- PMCID: PMC8042699
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-021-03768-8
Imaging manifestations of Caroli disease with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: a case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Both Caroli disease (CD) and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) are autosomal recessive disorders, which are more commonly found in infants and children, for whom surviving to adulthood is rare. Early diagnosis and intervention can improve the survival rate to some extent. This study adopted the case of a 26-year-old pregnant woman to explore the clinical and imaging manifestations and progress of CD concomitant with ARPKD to enable a better understanding of the disease.
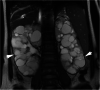
Case presentation: A 26-year-old pregnant woman was admitted to our hospital for more than 2 months following the discovery of pancytopenia and increased creatinine. Ultrasonography detected an enlarged left liver lobe, widened hepatic portal vein, splenomegaly, and dilated splenic vein. In addition, both kidneys were obviously enlarged and sonolucent areas of varying sizes were visible, but color Doppler flow imaging revealed no abnormal blood flow signals. The gestational age was approximately 25 weeks, which was consistent with the actual fetal age. Polyhydramnios was detected but no other abnormalities were identified. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed that the liver was plump, and polycystic liver disease was observed near the top of the diaphragm. The T1 and T2 weighted images were the low and high signals, respectively. The bile duct was slightly dilated; the portal vein was widened; and the spleen volume was enlarged. Moreover, the volume of both kidneys had increased to an abnormal shape, with multiple, long, roundish T1 and T2 abnormal signals being observed. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography revealed that intrahepatic cystic lesions were connected with intrahepatic bile ducts. The patient underwent a genetic testing, the result showed she carried two heterozygous mutations in PKHD1. The patient was finally diagnosed with CD with concomitant ARPKD. The baby underwent a genetic test three months after birth, the result showed that the patient carried one heterozygous mutations in PKHD1, which indicated the baby was a PKHD1 carrier.
Conclusions: This case demonstrates that imaging examinations are of great significance for the diagnosis and evaluation of CD with concomitant ARPKD.
Keywords: Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease; Caroli disease; Diagnosis; Magnetic resonance imaging; Ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Genetic diagnosis of Caroli syndrome with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: a case report and literature review].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Apr 18;50(2):335-339. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 29643536 Chinese.
-
Characteristics of congenital hepatic fibrosis in a large cohort of patients with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease.Gastroenterology. 2013 Jan;144(1):112-121.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.09.056. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23041322 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Caroli's syndrome with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease in a two month old infant.Yonsei Med J. 2006 Feb 28;47(1):131-4. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.1.131. Yonsei Med J. 2006. PMID: 16502495 Free PMC article.
-
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease: Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Management.Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2023 Sep;30(5):468-476. doi: 10.1053/j.akdh.2023.01.005. Adv Kidney Dis Health. 2023. PMID: 38097335 Review.
-
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease – PKHD1.2001 Jul 19 [updated 2024 Apr 4]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2001 Jul 19 [updated 2024 Apr 4]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301501 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Caroli disease incidentally discovered in a 23-years old male: A case report.Radiol Case Rep. 2024 Oct 4;20(1):1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.09.080. eCollection 2025 Jan. Radiol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39429706 Free PMC article.
-
Cholangitis resembling Caroli's syndrome in a patient with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Case report.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2025 Jun 6;13:2050313X251346657. doi: 10.1177/2050313X251346657. eCollection 2025. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40487302 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Choledochal Cyst: Insights from Genomics and Transcriptomics.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jun 8;13(6):1030. doi: 10.3390/genes13061030. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Potential Therapy Using Antisense Oligonucleotides to Treat Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 10;12(4):1428. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041428. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36835961 Free PMC article.
-
Caroli's Disease Associated with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease with Acute Pancreatitis: A Case Report.Middle East J Dig Dis. 2023 Oct;15(4):289-292. doi: 10.34172/mejdd.2023.360. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Middle East J Dig Dis. 2023. PMID: 38523883 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

