Functional cooperation between ASK1 and p21Waf1/Cip1 in the balance of cell-cycle arrest, cell death and tumorigenesis of stressed keratinocytes
- PMID: 33846306
- PMCID: PMC8042117
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-021-00459-3
Functional cooperation between ASK1 and p21Waf1/Cip1 in the balance of cell-cycle arrest, cell death and tumorigenesis of stressed keratinocytes
Abstract
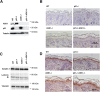
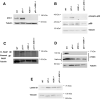
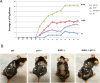
Both CDKN1A (p21 Waf1/Cip1) and Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) play important roles in tumorigenesis. The role of p21 Waf1/Cip1 in attenuating ASK1-induced apoptosis by various stress conditions is well established. However, how ASK1 and p21 Waf1/Cip1 functionally interact during tumorigenesis is still unclear. To address this aspect, we crossed ASK1 knockout (ASK1KO) mice with p21 Waf1/Cip1 knockout (p21KO) mice to compare single and double-mutant mice. We observed that deletion of p21 Waf1/Cip1 leads to increased keratinocyte proliferation but also increased cell death. This is mechanistically linked to the ASK1 axis-induced apoptosis, including p38 and PARP. Indeed, deletion of ASK1 does not alter the proliferation but decreases the apoptosis of p21KO keratinocytes. To analyze as this interaction might affect skin carcinogenesis, we investigated the response of ASK1KO and p21KO mice to DMBA/TPA-induced tumorigenesis. Here we show that while endogenous ASK1 is dispensable for skin homeostasis, ASK1KO mice are resistant to DMBA/TPA-induced tumorigenesis. However, we found that epidermis lacking both p21 and ASK1 reacquires increased sensitivity to DMBA/TPA-induced tumorigenesis. We demonstrate that apoptosis and cell-cycle progression in p21KO keratinocytes are uncoupled in the absence of ASK1. These data support the model that a critical event ensuring the balance between cell death, cell-cycle arrest, and successful divisions in keratinocytes during stress conditions is the p21-dependent ASK1 inactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Apoptosis inhibitory activity of cytoplasmic p21(Cip1/WAF1) in monocytic differentiation.EMBO J. 1999 Mar 1;18(5):1223-34. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.5.1223. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10064589 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Notch1-dependent p21(Waf1/Cip1) expression influences the Notch1 outcome in tumorigenesis.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(13):2046-55. doi: 10.4161/cc.29079. Epub 2014 May 6. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24801890 Free PMC article.
-
The role of p21(waf1/cip1) and p27(Kip1) in HDACi-mediated tumor cell death and cell cycle arrest in the Eμ-myc model of B-cell lymphoma.Oncogene. 2014 Nov 20;33(47):5415-23. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.482. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24292681
-
p21Cip1/Waf1 protein and its function based on a subcellular localization [corrected].J Cell Biochem. 2011 Dec;112(12):3502-6. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23296. J Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21815189 Review.
-
Differential effects of cell cycle regulatory protein p21(WAF1/Cip1) on apoptosis and sensitivity to cancer chemotherapy.Drug Resist Updat. 2003 Aug;6(4):183-95. doi: 10.1016/s1368-7646(03)00044-x. Drug Resist Updat. 2003. PMID: 12962684 Review.
Cited by
-
Updated insights on ASK1 signaling: mechanisms, regulation, and therapeutic potential in diseases.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun 14. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05330-y. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40515958 Review.
-
Engineering transcriptional regulatory networks for improving second-generation fuel ethanol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 28;10(1):207-217. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.10.006. eCollection 2025. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39558946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

