Constitutive depletion of Slc34a2/NaPi-IIb in rats causes perinatal mortality
- PMID: 33846411
- PMCID: PMC8042035
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-86874-z
Constitutive depletion of Slc34a2/NaPi-IIb in rats causes perinatal mortality
Abstract
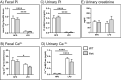
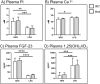
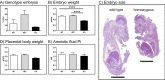
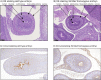
Absorption of dietary phosphate (Pi) across intestinal epithelia is a regulated process mediated by transcellular and paracellular pathways. Although hyperphosphatemia is a risk factor for the development of cardiovascular disease, the amount of ingested Pi in a typical Western diet is above physiological needs. While blocking intestinal absorption has been suggested as a therapeutic approach to prevent hyperphosphatemia, a complete picture regarding the identity and regulation of the mechanism(s) responsible for intestinal absorption of Pi is missing. The Na+/Pi cotransporter NaPi-IIb is a secondary active transporter encoded by the Slc34a2 gene. This transporter has a wide tissue distribution and within the intestinal tract is located at the apical membrane of epithelial cells. Based on mouse models deficient in NaPi-IIb, this cotransporter is assumed to mediate the bulk of active intestinal absorption of Pi. However, whether or not this is also applicable to humans is unknown, since human patients with inactivating mutations in SLC34A2 have not been reported to suffer from Pi depletion. Thus, mice may not be the most appropriate experimental model for the translation of intestinal Pi handling to humans. Here, we describe the generation of a rat model with Crispr/Cas-driven constitutive depletion of Slc34a2. Slc34a2 heterozygous rats were indistinguishable from wild type animals under standard dietary conditions as well as upon 3 days feeding on low Pi. However, unlike in humans, homozygosity resulted in perinatal lethality.
Conflict of interest statement
CAW has received honoraria and research grants from Bayer AG, Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, and Medice. The rest of the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


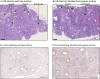
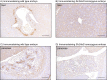
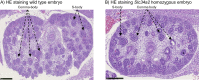
Similar articles
-
Intestinal Depletion of NaPi-IIb/Slc34a2 in Mice: Renal and Hormonal Adaptation.J Bone Miner Res. 2015 Oct;30(10):1925-37. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2523. Epub 2015 May 7. J Bone Miner Res. 2015. PMID: 25827490
-
1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 stimulates active phosphate transport but not paracellular phosphate absorption in mouse intestine.J Physiol. 2021 Feb;599(4):1131-1150. doi: 10.1113/JP280345. Epub 2020 Dec 8. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33200827
-
Expression of NaPi-IIb in rodent and human kidney and upregulation in a model of chronic kidney disease.Pflugers Arch. 2020 Apr;472(4):449-460. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02370-9. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Pflugers Arch. 2020. PMID: 32219532
-
The role of SLC34A2 in intestinal phosphate absorption and phosphate homeostasis.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Jan;471(1):165-173. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2221-1. Epub 2018 Oct 20. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 30343332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical aspects of the phosphate transporters NaPi-IIa and NaPi-IIb: mutations and disease associations.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Jan;471(1):137-148. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2246-5. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 30542787 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacology of Mammalian Na+-Dependent Transporters of Inorganic Phosphate.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;283:285-317. doi: 10.1007/164_2022_633. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 36592227
-
SRRM2 splicing factor modulates cell fate in early development.Biol Open. 2024 Apr 15;13(4):bio060415. doi: 10.1242/bio.060415. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 38656788 Free PMC article.
-
SLC34A2 Targets in Calcium/Phosphorus Homeostasis of Mammary Gland and Involvement in Development of Clinical Mastitis in Dairy Cows.Animals (Basel). 2024 Apr 24;14(9):1275. doi: 10.3390/ani14091275. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38731279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mc HG, Parsons DS. The absorption of water and salt from the small intestine of the rat. Q. J. Exp. Physiol. Cogn. Med. Sci. 1957;42(1):33–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

