Staphylococcus aureus vWF-binding protein triggers a strong interaction between clumping factor A and host vWF
- PMID: 33846500
- PMCID: PMC8041789
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-01986-6
Staphylococcus aureus vWF-binding protein triggers a strong interaction between clumping factor A and host vWF
Abstract
The Staphylococcus aureus cell wall-anchored adhesin ClfA binds to the very large blood circulating protein, von Willebrand factor (vWF) via vWF-binding protein (vWbp), a secreted protein that does not bind the cell wall covalently. Here we perform force spectroscopy studies on living bacteria to unravel the molecular mechanism of this interaction. We discover that the presence of all three binding partners leads to very high binding forces (2000 pN), largely outperforming other known ternary complexes involving adhesins. Strikingly, our experiments indicate that a direct interaction involving features of the dock, lock and latch mechanism must occur between ClfA and vWF to sustain the extreme tensile strength of the ternary complex. Our results support a previously undescribed mechanism whereby vWbp activates a direct, ultra-strong interaction between ClfA and vWF. This intriguing interaction represents a potential target for therapeutic interventions, including synthetic peptides inhibiting the ultra-strong interactions between ClfA and its ligands.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




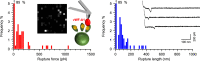

Similar articles
-
Clumping factor A, von Willebrand factor-binding protein and von Willebrand factor anchor Staphylococcus aureus to the vessel wall.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 May;15(5):1009-1019. doi: 10.1111/jth.13653. Epub 2017 Mar 23. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28182324 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Dual Role of Clumping Factor A in S. Aureus Adhesion to Endothelium in Absence and Presence of Plasma.Thromb Haemost. 2018 Jul;118(7):1230-1241. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1660435. Epub 2018 Jun 17. Thromb Haemost. 2018. PMID: 29909601
-
Marginal role of von Willebrand factor-binding protein and coagulase in the initiation of endocarditis in rats with catheter-induced aortic vegetations.Virulence. 2018;9(1):1615-1624. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1528845. Virulence. 2018. PMID: 30280967 Free PMC article.
-
The MSCRAMM Family of Cell-Wall-Anchored Surface Proteins of Gram-Positive Cocci.Trends Microbiol. 2019 Nov;27(11):927-941. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2019.06.007. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Trends Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31375310 Review.
-
Platelet-vessel wall interactions in thrombosis and restenosis role of von Willebrand factor.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1997;59(3):161-83. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1997. PMID: 9490916 Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus iron-regulated surface determinant B (IsdB) protein interacts with von Willebrand factor and promotes adherence to endothelial cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 23;11(1):22799. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02065-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34815454 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial interactions with platelets: defining key themes.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 3;16:1610289. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1610289. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40677721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the role of bacterial virulence factors and host elements in septic arthritis: insights from animal models for innovative therapies.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 12;15:1356982. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1356982. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38410388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibronectin binding protein B binds to loricrin and promotes corneocyte adhesion by Staphylococcus aureus.Nat Commun. 2022 May 6;13(1):2517. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30271-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35523796 Free PMC article.
-
Population distributions of single-cell adhesion parameters during the cell cycle from high-throughput robotic fluidic force microscopy.Sci Rep. 2022 May 11;12(1):7747. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11770-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35546603 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

