Deletion of LBR N-terminal domains recapitulates Pelger-Huet anomaly phenotypes in mouse without disrupting X chromosome inactivation
- PMID: 33846535
- PMCID: PMC8041748
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-01944-2
Deletion of LBR N-terminal domains recapitulates Pelger-Huet anomaly phenotypes in mouse without disrupting X chromosome inactivation
Abstract
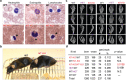
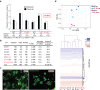
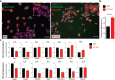
Mutations in the gene encoding Lamin B receptor (LBR), a nuclear-membrane protein with sterol reductase activity, have been linked to rare human disorders. Phenotypes range from a benign blood disorder, such as Pelger-Huet anomaly (PHA), affecting the morphology and chromatin organization of white blood cells, to embryonic lethality as for Greenberg dysplasia (GRBGD). Existing PHA mouse models do not fully recapitulate the human phenotypes, hindering efforts to understand the molecular etiology of this disorder. Here we show, using CRISPR/Cas-9 gene editing technology, that a 236bp N-terminal deletion in the mouse Lbr gene, generating a protein missing the N-terminal domains of LBR, presents a superior model of human PHA. Further, we address recent reports of a link between Lbr and defects in X chromosome inactivation (XCI) and show that our mouse mutant displays minor X chromosome inactivation defects that do not lead to any overt phenotypes in vivo. We suggest that our N-terminal deletion model provides a valuable pre-clinical tool to the research community and will aid in further understanding the etiology of PHA and the diverse functions of LBR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

