Risk factors and outcomes of diffuse alveolar haemorrhage after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 33846561
- PMCID: PMC8040008
- DOI: 10.1038/s41409-021-01293-y
Risk factors and outcomes of diffuse alveolar haemorrhage after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
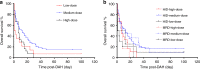
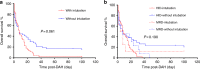
Diffuse alveolar haemorrhage (DAH) is a life-threatening pulmonary complication occurring after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) without an explicit aetiology or a standard treatment. This study aimed to explore the occurrence and prognosis of DAH after allo-HSCT, in addition to comparing discrepancies in the incidence, clinical characteristics and outcomes of DAH between patients undergoing haploidentical HSCT (HID-HSCT) and matched related donor HSCT (MRD-HSCT). We retrospectively evaluated 92 consecutive patients among 3987 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of DAH following allo-HSCT (HID: 71 patients, MRD: 21 patients). The incidence of DAH after allo-HSCT was 2.3%, 2.4% after HID-HSCT and 2.0% after MRD-HSCT (P = 0.501). The prognosis of patients with DAH after transplantation is extremely poor. The duration of DAH was 7.5 days (range, 1-48 days). The probabilities of overall survival (OS) were significantly different between patients with and without DAH within 2 years after transplantation (P < 0.001). According to the Cox regression analysis, a significant independent risk factor for the occurrence of DAH was delayed platelet engraftment (P < 0.001), and a high D-dimer level (>500 ng/ml) was a significant risk factor for the poor prognosis of DAH. HID-HSCT is similar to MRD-HSCT in terms of the outcomes of DAH.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Passweg JR, Baldomero H, Bader P, Bonini C, Duarte RF, Dufour C, et al. Use of haploidentical stem cell transplantation continues to increase: the 2015 European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplant activity survey report. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017;52:811–7. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2017.34. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

