Chromothripsis as an on-target consequence of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing
- PMID: 33846636
- PMCID: PMC8192433
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-021-00838-7
Chromothripsis as an on-target consequence of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing
Abstract
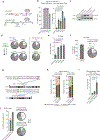
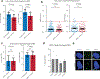
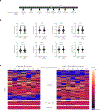
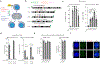
Genome editing has therapeutic potential for treating genetic diseases and cancer. However, the currently most practicable approaches rely on the generation of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), which can give rise to a poorly characterized spectrum of chromosome structural abnormalities. Here, using model cells and single-cell whole-genome sequencing, as well as by editing at a clinically relevant locus in clinically relevant cells, we show that CRISPR-Cas9 editing generates structural defects of the nucleus, micronuclei and chromosome bridges, which initiate a mutational process called chromothripsis. Chromothripsis is extensive chromosome rearrangement restricted to one or a few chromosomes that can cause human congenital disease and cancer. These results demonstrate that chromothripsis is a previously unappreciated on-target consequence of CRISPR-Cas9-generated DSBs. As genome editing is implemented in the clinic, the potential for extensive chromosomal rearrangements should be considered and monitored.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
M.J.W. is a consultant for Rubius Inc., Cellarity Inc., Beam Therapeutics, and Esperion; none of the consulting work is relevant to the current project. C.-Z. Z. is a scientific adviser for Pillar BioSciences. D.P. is a member of the Volastra Therapeutics scientific advisory board. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



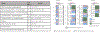

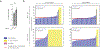


Comment in
-
CRISPR-Cas9 can cause chromothripsis.Nat Genet. 2021 Jun;53(6):768-769. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00881-4. Nat Genet. 2021. PMID: 34103715 No abstract available.
References
-
- Orkin SH & Bauer DE Emerging Genetic Therapy for Sickle Cell Disease. Annu Rev Med 70, 257–271 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

