Defining the lineage of thermogenic perivascular adipose tissue
- PMID: 33846639
- PMCID: PMC8136151
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-021-00380-0
Defining the lineage of thermogenic perivascular adipose tissue
Abstract
Brown adipose tissue can expend large amounts of energy, and therefore increasing its size or activity is a promising therapeutic approach to combat metabolic disease. In humans, major deposits of brown fat cells are found intimately associated with large blood vessels, corresponding to perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT). However, the cellular origins of PVAT are poorly understood. Here, we determine the identity of perivascular adipocyte progenitors in mice and humans. In mice, thoracic PVAT develops from a fibroblastic lineage, consisting of progenitor cells (Pdgfra+, Ly6a+ and Pparg-) and preadipocytes (Pdgfra+, Ly6a+ and Pparg+), which share transcriptional similarity with analogous cell types in white adipose tissue. Interestingly, the aortic adventitia of adult animals contains a population of adipogenic smooth muscle cells (Myh11+, Pdgfra- and Pparg+) that contribute to perivascular adipocyte formation. Similarly, human PVAT contains presumptive fibroblastic and smooth muscle-like adipocyte progenitor cells, as revealed by single-nucleus RNA sequencing. Together, these studies define distinct populations of progenitor cells for thermogenic PVAT, providing a foundation for developing strategies to augment brown fat activity.
Figures

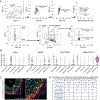

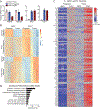



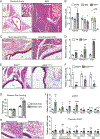

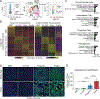
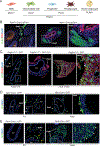
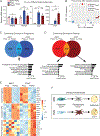


Comment in
-
Identification of thermogenic adipocyte lineages.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021 Jun;17(6):319. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00497-y. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33907309 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- K01 DK125608/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S06 GM008216/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK122808/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK120982/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141149/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK077097/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DK120062/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK019525/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK111714/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM121301/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK102898/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008216/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK123356/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK036836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

