Construction, petro-collecting/dispersing capacities, antimicrobial activity, and molecular docking study of new cationic surfactant-sulfonamide conjugates
- PMID: 33846661
- PMCID: PMC8026247
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116068
Construction, petro-collecting/dispersing capacities, antimicrobial activity, and molecular docking study of new cationic surfactant-sulfonamide conjugates
Abstract
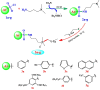
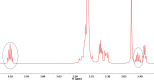
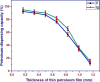
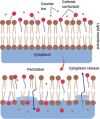
Surfactants with their diverse activities have been recently involved in controlling the spread of new coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic as they are capable of disrupting the membrane surrounding the virus. Using hybrids approach, we constructed a novel series of cationic surfactant-sulfonamide conjugates (3a-g) through quaternization of the as-prepared sulfonamide derivatives (2a-g) with n-hexadecyl iodide followed by structural characterization by spectroscopy (IR and NMR). Being collective properties required in petroleum-processing environment, the petro-collecting/dispersing capacities on the surface of waters with different degrees of mineralization, and the antimicrobial performance against microbes and sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) that mitigate microbiological corrosion were investigated for the synthesized conjugates. Among these conjugates, 3g (2.5% aq. solution) exhibited the strongest ability to disperse the thin petroleum film on the seawater surface, whereas KD is 95.33% after 96 h. In diluted form, 3f collected the petroleum layer on distilled water surface (Kmax = 32.01) for duration exceeds 4 days. Additionally, almost all compounds revealed high potency and comparable action with standard antimicrobials, especially 3b and 3f, which emphasize their role as potential biocides. Regarding biocidal activity against SRB, 3g causes a significant reduction in the bacterial count from 2.8 × 106 cells/mL to Nil. Moreover, the conducted molecular docking study confirms the strong correlation between RNA polymerase binding with bioactivity against microbes over other studied proteins (threonine synthase and cyclooxygenase-2).
Keywords: Biocidal activity; Cationic surfactants; Molecular docking; Petro-collecting; Petro-dispersing; Sulfonamides.
© 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Petroleum-collecting and dispersing complexes based on oleic acid and nitrogenous compounds as surface-active agents for removing thin petroleum films from water surface.J Oleo Sci. 2012;61(11):621-30. doi: 10.5650/jos.61.621. J Oleo Sci. 2012. PMID: 23138251
-
Crystallographic study, biological assessment and POM/Docking studies of pyrazoles-sulfonamide hybrids (PSH): Identification of a combined Antibacterial/Antiviral pharmacophore sites leading to in-silico screening the anti-Covid-19 activity.J Mol Struct. 2022 Nov 5;1267:133605. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133605. Epub 2022 Jun 28. J Mol Struct. 2022. PMID: 35782312 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of A Cationic Surfactant by Capping Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Multiple Applications.Molecules. 2020 Apr 25;25(9):2007. doi: 10.3390/molecules25092007. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32344868 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid-sulfonamide conjugates as antibacterial agents: design, synthesis and molecular docking studies.RSC Adv. 2020 Nov 25;10(70):42983-42992. doi: 10.1039/d0ra09051d. eCollection 2020 Nov 23. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35514930 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactants as Antimicrobials: A Brief Overview of Microbial Interfacial Chemistry and Surfactant Antimicrobial Activity.J Surfactants Deterg. 2019 Sep;22(5):1119-1127. doi: 10.1002/jsde.12293. Epub 2019 Jun 4. J Surfactants Deterg. 2019. PMID: 32336911 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proton transfer induced excited-state aromaticity gain for chromophores with maximal Stokes shifts.Chem Sci. 2024 Oct 2;15(43):17918-26. doi: 10.1039/d4sc04692g. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39397815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee S., Lee J., Yu H., Lim J. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016;38:157–166.
-
- Hasanov E.E., Rahimov R.A., Abdullayev Y., Asadov Z.H., Ahmadova G.A., Isayeva A.M., Ahmadbayova S.F., Zubkov F.I., Autschbach J. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020;86:123–135.
-
- Danish M., Ashiq M., Nazar M.F. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 2017;38:837–844.
-
- García M.T., Campos E., Sanchez-Leal J., Ribosa I. Chemosphere. 1999;38:3473–3483. - PubMed
-
- A.S. Kalgutkar, R. Jones, A. Sawant, in Sulfonamide as an Essential Functional Group in Drug Design, D.A. Smith Ed., pp. 210-274, Royal Society of Chemistry, (2010).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
