Long non‑coding RNA MIR4435‑2HG promotes the progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the miR‑383‑5p/RBM3 axis
- PMID: 33846802
- PMCID: PMC8054316
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2021.8050
Long non‑coding RNA MIR4435‑2HG promotes the progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the miR‑383‑5p/RBM3 axis
Abstract
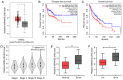
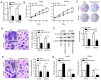
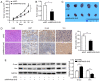
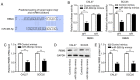
Recent studies have shown that long non‑coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are strongly related to the progression of various types of cancer. The lncRNA MIR4435‑2 host gene (MIR4435‑2HG) has been recently recognized as a tumor‑related lncRNA that is upregulated in several tumors. However, its possible functions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remain unclear. In tShe present study, we observed that MIR4435‑2HG expression was markedly upregulated in HNSCC tissues based on a Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis dataset. This result was further confirmed in HNSCC tissues and cell lines using quantitative real‑time polymerase chain reaction. In addition, the high expression level of MIR4435‑2HG was significantly associated with poor disease‑free survival and overall survival in all HNSCC cases and was associated with advanced tumor‑metastasis‑node stage and poor prognosis. In vitro and in vivo assays demonstrated that MIR4435‑2HG knockdown suppressed HNSCC cell proliferation and invasion, epithelial‑mesenchymal transition (EMT), and tumor growth as determined by Cell Counting Kit‑8, Transwell assays and western blotting. Furthermore, MIR4435‑2HG affected HNSCC cell proliferation and migration and EMT by modulating the microRNA miR‑383‑5p to positively regulate the protein expression level of RNA‑binding motif protein 3 (RBM3). In conclusion, we provide a detailed analysis of the roles of MIR4435‑2HG in HNSCC and identified the MIR4435‑2HG/miR‑383‑5p/RBM3 axis as a potential therapeutic target for HNSCC treatment.
Keywords: MIR4435‑2HG; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; cell proliferation; cell migration; epithelial–mesenchymal transition; miR‑383‑5p/RBM3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Liu S, Zhang J, Yin L, Wang X, Zheng Y, Zhang Y, Gu J, Yang L, Yang J, Zheng P, et al. The lncRNA RUNX1-IT1 regulates C-FOS transcription by interacting with RUNX1 in the process of pancreatic cancer proliferation, migration and invasion. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:412. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2617-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

