MicroRNA‑485‑5p suppresses the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting flotillin‑1 and inhibits the epithelial‑mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 33846817
- PMCID: PMC8047942
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2021.8044
MicroRNA‑485‑5p suppresses the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting flotillin‑1 and inhibits the epithelial‑mesenchymal transition
Abstract
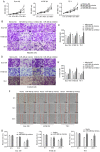
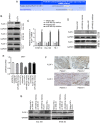
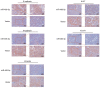
As esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers in Asia, it is crucial to uncover its underlying molecular mechanisms that support its development and progression. Several articles have reported that microRNA (miR)‑485‑5p inhibits the malignant phenotype in a number of cancer types, such as lung, gastric and breast cancer, but to the best of our knowledge, its function in ESCC has not been studied in depth until the present study. It is of great significance to probe the regulatory action and underlying mechanism of miR‑485‑5p in ESCC. In brief, this study identified that miR‑485‑5p expression in ESCC tissues was significantly lower than that in normal tissues. The decrease in miR‑485‑5p expression was associated with a larger tumour size and poor histology and stage. The expression of miR‑485‑5p was relatively high in Eca 109 and TE‑1 cells, but relatively low in KYSE 30. The overexpression of miR‑485‑5p inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro, whereas miR‑485‑5p knockdown did the opposite. Flotillin‑1 (FLOT‑1) can facilitate the malignant phenotype in various cancer types. The present study found that in ESCC tissue, the protein expression of FLOT‑1 was negatively correlated with miR‑485‑5p expression. Further experiments showed that miR‑485‑5p directly targeted the 3'‑untranslated region of FLOT‑1. The overexpression of miR‑485‑5p significantly suppressed the mRNA and protein expression levels of FLOT‑1, whereas knockdown had the reverse effects. Furthermore, overexpression of miR‑485‑5p restrained epithelial‑mesenchymal metastasis (EMT)‑related factors at both the mRNA and protein levels. At the same time, it also inhibited the growth of ESCC and restrained the EMT in vivo. In summary, miR‑485‑5p was found to be an inhibitor of ESCC and may have potential as a novel target candidate for ESCC treatment.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; expression; miR‑485‑5p; FLOT‑1; clinicopathological features.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs: A novel signature in the metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 21;30(11):1497-1523. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1497. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38617454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 induces proliferation, migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and stemness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via post-transcriptional regulation of BMI1 and CTNNB1.Mol Oncol. 2020 Sep;14(9):2332-2351. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12683. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32239639 Free PMC article.
-
miR-25 mediates metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal-transition in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via regulation of E-cadherin signaling.Bioengineered. 2019 Dec;10(1):679-688. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2019.1687391. Bioengineered. 2019. PMID: 31679450 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circNTRK2 facilitates the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through up-regulating NRIP1 expression via miR-140-3p.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jul 11;39(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01640-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32653032 Free PMC article.
-
TP53 Mutations in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Sep 24;28(9):219. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2809219. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37796679 Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA PKMYT1AR promotes cancer stem cell maintenance in non-small cell lung cancer via activating Wnt signaling pathway.Mol Cancer. 2021 Dec 2;20(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01469-6. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34856993 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: A novel signature in the metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 21;30(11):1497-1523. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1497. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38617454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non‑coding RNA: A promising diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (Review).Oncol Lett. 2024 Apr 9;27(6):255. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14388. eCollection 2024 Jun. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38646493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC00704 boosts the immunologic escape of colorectal cancer cells by upregulating TLR4 by binding with miR- 203a- 3p.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Apr 10;30(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02514-6. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40211393 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs Associated with Androgen Receptor and Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 4;16(3):665. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030665. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brock MV, Gou M, Akiyama Y, Muller A, Wu TT, Montgomery E, Deasel M, Germonpré P, Rubinson L, Heitmiller RF, et al. Prognostic importance of promoter hypermethylation of multiple genes in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:2912–2919. - PubMed
-
- Thrumurthy SG, Chaudry MA, Thrumurthy SSD, Mughal M. Oesophageal cancer: Risks, prevention, and diagnosis. BMJ. 2019;366:14373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

