Clinical Application of the Standard Q COVID-19 Ag Test for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- PMID: 33847084
- PMCID: PMC8042480
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e101
Clinical Application of the Standard Q COVID-19 Ag Test for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
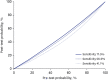
We evaluated the Standard Q COVID-19 Ag test for the diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) compared to the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test. We applied both tests to patients who were about to be hospitalized, had visited an emergency room, or had been admitted due to COVID-19 confirmed by RT-PCR. Two nasopharyngeal swabs were obtained; one was tested by RT-PCR and the other by the Standard Q COVID-19 Ag test. A total of 118 pairs of tests from 98 patients were performed between January 5 and 11, 2021. The overall sensitivity and specificity for detecting severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) for the Standard Q COVID-19 Ag test compared to RT-PCR were 17.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 8.8-32.0%) and 100% (95% CI, 95.3-100.0%). Analysis of the results using RT-PCR cycle thresholds of ≤ 30 or ≤ 25 increased the sensitivity to 26.9% (95% CI, 13.7-46.1%), and 41.1% (95% CI, 21.6-64.0%), respectively.
Keywords: Antigen Test; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- CDC's diagnostic test for COVID-19 only and supplies. [Updated December 9, 2020]. [Accessed January 27, 2021]. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/virus-requests.html.
-
- Turcato G, Zaboli A, Pfeifer N, Ciccariello L, Sibilio S, Tezza G, et al. Clinical application of a rapid antigen test for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients evaluated in the emergency department: a preliminary report. J Infect. 2021;82(3):e14–6. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous