Experimental and Ab Initio Characterization of Mononuclear Molybdenum Dithiocarbamates in Lubricant Mixtures
- PMID: 33847121
- PMCID: PMC8154871
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c00029
Experimental and Ab Initio Characterization of Mononuclear Molybdenum Dithiocarbamates in Lubricant Mixtures
Abstract
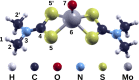
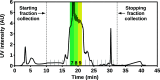
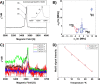
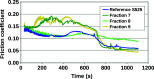
Molybdenum dithiocarbamates (MoDTCs) are a class of lubricant additives widely employed in automotives. Most of the studies concerning MoDTC take into account the dimeric structures because of their industrial relevance, with the mononuclear compounds usually neglected, because isolating and characterizing subgroups of MoDTC molecules are generally difficult. However, the byproducts of the synthesis of MoDTC can impact the friction reduction performance at metallic interfaces, and the effect of mononuclear MoDTC (mMoDTC) compounds in the lubrication has not been considered yet in the literature. In this study, we consider for the first time the impurities of MoDTC consisting of mononuclear compounds and combine experimental and computational techniques to elucidate the interaction of these impurities with binuclear MoDTC in commercial formulations. We present a preliminary strategy to separate a commercial MoDTC product in chemically different fractions. These fractions present different tribological behaviors depending on the relative amount of mononuclear and binuclear complexes. The calculations indicate that the dissociation mechanism of mMoDTC is similar to the one observed for the dimeric structures. However, the different chemical properties of mMoDTC impact the kinetics for the formation of the beneficial molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) layers, as shown by the tribological experiments. These results help to understand the functionality of MoDTC lubricant additives, providing new insights into the complex synergy between the different chemical structures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Holmberg K.; Erdemir A. Influence of Tribology on Global Energy Consumption, Costs and Emissions. Friction 2017, 5, 263–284. 10.1007/s40544-017-0183-5. - DOI
-
- Spikes H. Friction Modifier Additives. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 60, 5.10.1007/s11249-015-0589-z. - DOI
-
- Guegan J.; Southby M.; Spikes H. Friction Modifier Additives, Synergies and Antagonisms. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 83.10.1007/s11249-019-1198-z. - DOI
-
- Yamamoto Y.; Gondo S. Friction and Wear Characteristics of Molybdenum Dithiocarbamate and Molybdenum Dithiophosphate. Tribol. Trans. 1989, 32, 251–257. 10.1080/10402008908981886. - DOI
-
- Grossiord C.; Varlot K.; Martin J.-M.; Le Mogne T.; Esnouf C.; Inoue K. MoS2 Single Sheet Lubrication by Molybdenum Dithiocarbamate. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 737–743. 10.1016/s0301-679x(98)00094-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

