Clinical, laboratory, and imaging features of pediatric COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33847620
- PMCID: PMC8052054
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025230
Clinical, laboratory, and imaging features of pediatric COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
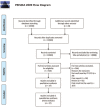
Pediatric cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have been reported. This meta-analysis was aimed at describing the clinical, laboratory, and imaging characteristics of children with COVID-19 based on published data of pediatric COVID-19 cases.Search of PubMed, Embase, Web of Sciences, Science Direct, and Google Scholar for articles published until December 14, 2020, that described the clinical, laboratory, and imaging features of children with COVID-19. Data were extracted independently by 2 authors. Random-effects meta-analysis models were used to report pooled results.Clinical data from 2874 children with COVID-19 from 37 articles were finally included for quantitative analyses. Fever (48.5%, 95% CI: 41.4%-55.6%) and cough (40.6%, 95% CI: 33.9%-47.5%) were the most common symptoms; asymptomatic infection and severe cases, respectively, accounted for 27.7% (95% CI: 19.7%-36.4%) patients and 1.1% of the 1933 patients included. Laboratory tests showed 5.5% (95% CI: 2.8%-8.9%) of the patients had lymphopenia. The pooled prevalence of leukopenia was 7.3% (95% CI: 3.4%-12.2%), and the C-reactive protein level was high in 14.0% (95% CI: 6.8%-22.8%). Chest computed tomography showed unilateral and bilateral lesions, and ground-glass opacity in 29.4% (95% CI: 24.8%-34.3%) and 24.7% (95% CI: 18.2%-31.6%), and 32.9% (95% CI: 25.3%-40.9%), respectively, and normal in approximately 36.0% (95% CI: 27.7%-44.7%).We found that children with COVID-19 had relatively mild disease, with quite a lot of asymptomatic infections and low rate of severe illness. Data from more regions are needed to determine the prevention and treatment strategies for children with COVID-19.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak 2020. 2020; https://www.who.int. [access date 04 October, 2020].
-
- World Health Organization. Critical preparedness, readiness and response actions for COVID-19. 2020; https://www.who.int/publications-detail/critical-preparedness-readiness-.... [access date 02 October, 2020].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials