Oral Pharmacokinetics in Beagle Dogs of the Mitragynine Metabolite, 7-Hydroxymitragynine
- PMID: 33847897
- PMCID: PMC8179724
- DOI: 10.1007/s13318-021-00684-2
Oral Pharmacokinetics in Beagle Dogs of the Mitragynine Metabolite, 7-Hydroxymitragynine
Abstract
Background and objectives: 7-Hydroxymitragynine (7-HMG) is an oxidative metabolite of mitragynine, the most abundant alkaloid in the leaves of Mitragyna speciosa (otherwise known as kratom). While mitragynine is a weak partial µ-opioid receptor (MOR) agonist, 7-HMG is a potent and full MOR agonist. It is produced from mitragynine by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A, a drug-metabolizing CYP isoform predominate in the liver that is also highly expressed in the intestine. Given the opioidergic potency of 7-HMG, a single oral dose pharmacokinetic and safety study of 7-HMG was performed in beagle dogs.
Methods: Following a single oral dose (1 mg/kg) of 7-HMG, plasma samples were obtained from healthy female beagle dogs. Concentrations of 7-HMG were determined using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a tandem mass spectrometer (UPLC-MS/MS). Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using a model-independent non-compartmental analysis of plasma concentration-time data.
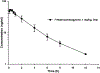
Results: Absorption of 7-HMG was rapid, with a peak plasma concentration (Cmax, 56.4 ± 1.6 ng/ml) observed within 15 min post-dose. In contrast, 7-HMG elimination was slow, exhibiting a mono-exponential distribution and mean elimination half-life of 3.6 ± 0.5 h. Oral dosing of 1 mg/kg 7-HMG was well tolerated with no observed adverse events or significant changes to clinical laboratory tests.
Conclusions: These results provide the first pharmacokinetic and safety data for 7-HMG in the dog and therefore contribute to the understanding of the putative pharmacologic role of 7-HMG resulting from an oral delivery of mitragynine from kratom.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Makary MA, Overton HN, Wang P. Overprescribing is major contributor to opioid crisis. BMJ. 2017:359:j4792. - PubMed
-
- Rummans TA, Burton MC, Dawson NL. How good intentions contributed to bad outcomes: the opioid crisis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018;93(3):344–50. - PubMed
-
- Vadivelu N, Kai AM, Kodumudi V, Sramcik J, Kaye AD. The opioid crisis: a comprehensive overview. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018;22(3):16. - PubMed
-
- Singh D, Narayanan S, Vicknasingam B. Traditional and non-traditional uses of Mitragynine (Kratom): A survey of the literature. Brain Res Bull. 2016;126:41–6. - PubMed
-
- Ward J, Rosenbaum C, Hernon C, McCurdy CR, Boyer EW. Herbal medicines for the management of opioid addiction. CNS Drugs. 2011;25(12):999–1007. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources