Impact of COVID-19 on education, health and lifestyle behaviour of Brazilian urology residents
- PMID: 33848067
- PMCID: PMC8321480
- DOI: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2021.99.09
Impact of COVID-19 on education, health and lifestyle behaviour of Brazilian urology residents
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on clinical and surgical practice, educational activities, health and lifestyle behavior of Brazilian urology residents.
Materials and methods: A web-based survey was sent to 468 Brazilian urology residents from postgraduate years (PGY) 3 to 5 to collect data on clinical practice and training after 4 months of COVID-19. We also assessed health-related and behavior changes, rate of infection by SARS-CoV-2, deployment to the front line of COVID-19, residents' concerns, and access to personal protective equipment (PPE).
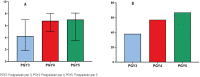
Results: Massive reductions in elective and emergency patient consultations, diagnostic procedures and surgeries were reported across the country, affecting PGY 3 to 5 alike. Most in-person educational activities were abolished. The median damage to the urological training expected for 2020 was 6.0 [3.4 -7.7], on a scale from 0 to 10, with senior residents estimating a greater damage (P < 0.001). Educational interventions developed included online case-based discussions, subspeciality conferences and lectures, and grand rounds. Most senior residents favored extending residency to compensate for training loss and most younger residents favored no additional training (p< 0.001). Modifications in health and lifestyle included weight gain (43.8%), reduced physical activity (68.6%), increased alcoholic intake (44.9%) and cigarette consumption (53.6%), worsening of sexual life (25.2%) and feelings of sadness or depression (48,2%). Almost half were summoned to work on the COVID-19 front-line and 24.4% had COVID-19. Most residents had inadequate training to deal with COVID-19 patients and most reported a shortage of PPE. Residents' concerns included the risk of contaminating family members, being away from residency program, developing severe COVID-19 and overloading colleagues.
Conclusions: COVID-19 had a massive impact in Brazilian urology residents´ training, health and lifestyle behavior, which may reflect what happened in other medical specialties. Studies should confirm these findings to help developing strategies to mitigate residents' losses.
Keywords: COVID-19; Education, Medical; Surveys and Questionnaires.
Copyright® by the International Brazilian Journal of Urology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- 1. Ficarra V, Novara G, Abrate A, Bartoletti R, Crestani A, De Nunzio C, et al. Urology practice during the COVID-19 pandemic. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2020;72:369-75. - PubMed
-
- 3. Amparore D, Claps F, Cacciamani GE, Esperto F, Fiori C, Liguori G, et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on urology residency training in Italy. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2020;72:505-9. - PubMed
-
- 4. Rosen GH, Murray KS, Greene KL, Pruthi RS, Richstone L, Mirza M. Effect of COVID-19 on Urology Residency Training: A Nationwide Survey of Program Directors by the Society of Academic Urologists. J Urol. 2020;204:1039-45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous