Does successful urethral calibration rule out significant female urethral stenosis? confronting the confounder- an outcome analysis of successfully treated female urethral strictures
- PMID: 33848077
- PMCID: PMC8321492
- DOI: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.0857
Does successful urethral calibration rule out significant female urethral stenosis? confronting the confounder- an outcome analysis of successfully treated female urethral strictures
Abstract
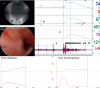
Objective: The diagnosis and treatment of female urethral stricture disease (FUSD) are practiced variably due to the scarcity of data on evaluation, variable definitions, and lack of long-term surgical outcomes. FUSD is difficult to rule out solely on the basis of a successful calibration with 14F catheter. In this study, we have tried to characterize the variable clinical presentation of FUSD, the diagnostic utility of calibration, videourodynamic study(VUDS), and urethroscopy in planning surgical management.
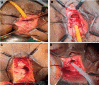
Materials and methods: A retrospective review of records of 16 patients who underwent surgical management of FUSD was analyzed. The clinical history, examination findings, and the results of all the investigations (including uroflowmetry, VUDS findings, urethroscopy) they underwent, the procedures they had undergone ,and the follow-up data were studied.
Results: A total of 16 patients underwent surgical management of FUSD. 13 out of 16 patients had successful calibration with 14F catheter on the initial presentation. These 13 patients on VUDS demonstrated significant BOO and had variable stigmata of stricture on urethroscopy. The mean IPSS, flow rate, and PVR at presentation and after urethroplasty were 23.88±4.95, 7.72±4.25mL/s, 117.06±74.46mL and 3.50±3.44, 22.34±4.80mL/s, and 12.50±8.50mL, respectively. (p < 0.05). The mean flow rate after endo dilation(17F) (n=12) was 11.4±2.5mL/s while after urethroplasty improved to 20.30±4.19mL/s and was statistically significant(p < 0.05).
Conclusions: An adept correlation between clinical assessment, urethroscopy findings, and VUDS is key in objectively identifying FUSD and planning surgical management. A good caliber of the urethra is not sufficient enough to rule out a significant obstruction due to FUSD. Early urethroplasty provides significantly better outcomes in patients who have failed dilation as a treatment.
Keywords: Urinary Bladder; Female; Urethral Stricture.
Copyright® by the International Brazilian Journal of Urology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Comment in
-
Editorial Comment: Does successful urethral calibration rule out significant female urethral stenosis? confronting the confounder- an outcome analysis of successfully treated female urethral strictures.Int Braz J Urol. 2021 Jul-Aug;47(4):841-842. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.0857.1. Int Braz J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33848078 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Story of Female Urethral Stricture - "To a man with a hammer, everything looks like a nail".Int Braz J Urol. 2021 Nov-Dec;47(6):1281-1283. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2021.0292. Int Braz J Urol. 2021. PMID: 34469680 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- 2. Kuo HC. Videourodynamic characteristics and lower urinary tract symptoms of female bladder outlet obstruction. Urology. 2005; 66:1005-9. - PubMed
-
- 3. Osman NI, Mangera A, Chapple CR. A systematic review of surgical techniques used in the treatment of female urethral stricture. Eur Urol. 2013; 64:965-73. - PubMed
-
- 4. Spilotros M, Malde S, Solomon E, Grewal M, Mukhtar BM, Pakzad M, et al. Female urethral stricture: a contemporary series. World J Urol. 2017; 35:991-995. - PubMed
-
- 5. Gormley EA. Vaginal flap urethroplasty for female urethral stricture disease. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29(Suppl 1):S42-5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
