Long-Term Outcomes of Dose-Escalated Pelvic Lymph Node Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) With a Simultaneous Hypofractionated Boost to the Prostate for Very High-Risk Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: A Prospective Phase II Clinical Trial
- PMID: 33848618
- PMCID: PMC8638529
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prro.2021.03.006
Long-Term Outcomes of Dose-Escalated Pelvic Lymph Node Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) With a Simultaneous Hypofractionated Boost to the Prostate for Very High-Risk Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: A Prospective Phase II Clinical Trial
Abstract
Purpose: There remains limited data as to the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of higher doses of elective radiation therapy to the pelvic lymph nodes in men with high-risk prostate cancer. We conducted a phase II study to evaluate moderate dose escalation to the pelvic lymph nodes using a simultaneous integrated boost to the prostate.
Methods and materials: Patients were eligible with biopsy-proven adenocarcinoma of the prostate, a calculated lymph node risk of at least 25%, Karnofsky performance scale ≥70, and no evidence of M1 disease. Acute and late toxicity were prospectively collected at each follow-up using Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.0 (CTCAE v4.0). The pelvic lymph nodes were treated to a dose of 56 Gy over 28 fractions with a simultaneous integrated boost to the prostate to a total dose of 70 Gy over 28 fractions using intensity-modulated radiation therapy.
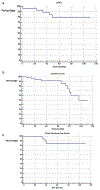
Results: Thirty patients were prospectively enrolled from October 2010 to August 2014. Median patient age was 70 years (57-83), pretreatment prostate-specific antigen was 11.5 ng/mL (3.23-111.5), T stage was T2c (T1c-T3b), and Gleason score was 9 (6-9). CTCAE v4.0 rate of any grade 1 or 2 genitourinary and gastrointestinal toxicity were 55% and 44%, respectively, and there was 1 reported acute grade 3 genitourinary and gastrointestinal toxicity, both unrelated to protocol therapy. With a median follow-up of 6.4 years, the biochemical failure free survival rate was 80.2%, and mean biochemical progression free survival was 8.3 years (95% confidence interval [CI], 7.2-9.4). The prostate cancer specific survival was 95.2%, and mean prostate cancer specific survival was 8.7 years (95% CI, 8.0-9.4). Five-year distant metastases free survival was 96%. Medians were not reached.
Conclusions: In this single arm, small, prospective feasibility study, nodal radiation therapy dose escalation was safe, feasible, and seemingly well tolerated. Rates of progression free survival are highly encouraging in this population of predominately National Comprehensive Cancer Network very high-risk patients.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- He J, Albertsen PC, Moore D, Rotter D, Demissie K, Lu-Yao G. Validation of a contemporary five-tiered Gleason grade grouping using population-based data. Eur Urol. 2017;71:760–763. - PubMed
-
- Zietman AL, Bae K, Slater JD, et al. Randomized trial comparing conventional-dose with high-dose conformal radiation therapy in early-stage adenocarcinoma of the prostate: Long-term results from proton radiation oncology group/american college of radiology 95-09. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1106–1111. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical