Clinical COVID-19 diagnostic methods: Comparison of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) and quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
- PMID: 33848785
- PMCID: PMC7997201
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104813
Clinical COVID-19 diagnostic methods: Comparison of reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) and quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is a major public health concern. Accurate and rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 is critical for disease control. Reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) is a nucleic acid amplification assay similar to reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), the former being a simple, low cost, and rapid method.
Objectives: This study aimed to compare the RT-LAMP assay with RT-PCR using the Loopamp™ SARS-CoV-2 Detection Kit.
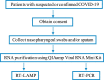
Study design: One hundred and fifty-one nasopharyngeal swab and 88 sputum samples obtained from individuals with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 were examined.
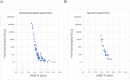
Results: RT-LAMP had high specificity (98.5 % (95 % CI: 96.9-100 %)), sensitivity (87.0 % (95 % CI: 82.8-91.3 %)), positive predictive value (97.9 % (95 % CI: 96.1-99.7 %)), negative predictive value (90.2 % (95 % CI: 86.4-94.0 %)), and concordance rate (93.3 % (95 % CI: 90.1-96.5 %)). Nasopharyngeal and sputum samples positive in RT-LAMP contained as few as 10.2 and 23.4 copies per 10 μL, respectively. RT-LAMP showed similar performance to RT-PCR for samples with cycle threshold value below 36.
Conclusions: These results indicate that RT-LAMP is a highly reliable and at least equivalent to RT-PCR in utility, and potentially applicable in settings that are more diverse as a point-of-care tool.
Keywords: COVID-19; Diagnosis; Polymerase chain reaction; RT-LAMP; SARS-CoV-2; Sputum.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letter of concern on evaluating the consistency between two clinical COVID-19 diagnostic methods.J Clin Virol. 2022 Sep;154:105241. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2022.105241. Epub 2022 Jul 11. J Clin Virol. 2022. PMID: 35843071 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Multisite Clinical Validation of Isothermal Amplification-Based SARS-CoV-2 Detection Assays Using Different Sampling Strategies.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0084621. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00846-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34668736 Free PMC article.
-
Isothermal amplification and fluorescent detection of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2 variant virus in nasopharyngeal swabs.PLoS One. 2021 Sep 17;16(9):e0257563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257563. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34534259 Free PMC article.
-
A semi-automated, isolation-free, high-throughput SARS-CoV-2 reverse transcriptase (RT) loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) test.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 1;11(1):21385. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00827-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34725400 Free PMC article.
-
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): An effective molecular point-of-care technique for the rapid diagnosis of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.Rev Med Virol. 2021 Nov;31(6):e2215. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2215. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Rev Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33476080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleic Acid Testing of SARS-CoV-2.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 7;22(11):6150. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116150. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34200331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep Fractional Max Pooling Neural Network for COVID-19 Recognition.Front Public Health. 2021 Aug 10;9:726144. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.726144. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. Retraction in: Front Public Health. 2024 Jan 03;11:1358295. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1358295. PMID: 34447739 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The critical role of mesenchymal stromal/stem cell therapy in COVID-19 patients: An updated review.Cell Biochem Funct. 2021 Dec;39(8):945-954. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3670. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021. PMID: 34545605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detecting COVID-19.J Clin Virol Plus. 2023 Feb;3(1):100132. doi: 10.1016/j.jcvp.2022.100132. Epub 2022 Dec 29. J Clin Virol Plus. 2023. PMID: 36594046 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter evaluation of a simple and sensitive nucleic acid self-testing for SARS-CoV-2.Virol Sin. 2023 Aug;38(4):620-626. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.06.009. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Virol Sin. 2023. PMID: 37406815 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical paper-based antigen sensing platform using plant-derived monoclonal antibody for detecting SARS-CoV-2.Talanta. 2023 Jan 1;251:123783. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123783. Epub 2022 Aug 7. Talanta. 2023. PMID: 35977451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2020. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard.https://covid19.who.int/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

