Global RNA profiles show target selectivity and physiological effects of peptide-delivered antisense antibiotics
- PMID: 33849070
- PMCID: PMC8096218
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab242
Global RNA profiles show target selectivity and physiological effects of peptide-delivered antisense antibiotics
Abstract
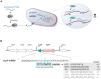
Antisense peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) inhibiting mRNAs of essential genes provide a straight-forward way to repurpose our knowledge of bacterial regulatory RNAs for development of programmable species-specific antibiotics. While there is ample proof of PNA efficacy, their target selectivity and impact on bacterial physiology are poorly understood. Moreover, while antibacterial PNAs are typically designed to block mRNA translation, effects on target mRNA levels are not well-investigated. Here, we pioneer the use of global RNA-seq analysis to decipher PNA activity in a transcriptome-wide manner. We find that PNA-based antisense oligomer conjugates robustly decrease mRNA levels of the widely-used target gene, acpP, in Salmonella enterica, with limited off-target effects. Systematic analysis of several different PNA-carrier peptides attached not only shows different bactericidal efficiency, but also activation of stress pathways. In particular, KFF-, RXR- and Tat-PNA conjugates especially induce the PhoP/Q response, whereas the latter two additionally trigger several distinct pathways. We show that constitutive activation of the PhoP/Q response can lead to Tat-PNA resistance, illustrating the utility of RNA-seq for understanding PNA antibacterial activity. In sum, our study establishes an experimental framework for the design and assessment of PNA antimicrobials in the long-term quest to use these for precision editing of microbiota.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A comparative analysis of peptide-delivered antisense antibiotics using diverse nucleotide mimics.RNA. 2024 May 16;30(6):624-643. doi: 10.1261/rna.079969.124. RNA. 2024. PMID: 38413166 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense inhibition of gene expression and growth in gram-negative bacteria by cell-penetrating peptide conjugates of peptide nucleic acids targeted to rpoD gene.Biomaterials. 2012 Jan;33(2):659-67. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.09.075. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Biomaterials. 2012. PMID: 22000398
-
Uptake, Stability, and Activity of Antisense Anti-acpP PNA-Peptide Conjugates in Escherichia coli and the Role of SbmA.ACS Chem Biol. 2021 Mar 19;16(3):471-479. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.0c00822. Epub 2021 Mar 8. ACS Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 33684286
-
Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) antisense effect to bacterial growth and their application potentiality in biotechnology.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Mar;86(2):397-402. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2387-8. Epub 2010 Feb 5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20135118 Review.
-
Antibacterial Peptide Nucleic Acids-Facts and Perspectives.Molecules. 2020 Jan 28;25(3):559. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030559. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32012929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selected strategies to fight pathogenic bacteria.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2155816. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2155816. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36629427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comparative analysis of peptide-delivered antisense antibiotics using diverse nucleotide mimics.RNA. 2024 May 16;30(6):624-643. doi: 10.1261/rna.079969.124. RNA. 2024. PMID: 38413166 Free PMC article.
-
RNA toehold switch-based reporter assay to assess bacterial uptake of antisense oligomers.mBio. 2025 Apr 9;16(4):e0398324. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03983-24. Epub 2025 Mar 4. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40035593 Free PMC article.
-
A (metaphorical) moment for RNA-based biotechnology? : Current metaphors for RNA limit development of and public communication about RNA-based technologies.EMBO Rep. 2024 Aug;25(8):3182-3186. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00200-y. Epub 2024 Jul 8. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 38977892 Free PMC article.
-
ASOBIOTICS 2024: an interdisciplinary symposium on antisense-based programmable RNA antibiotics.RNA. 2025 Mar 18;31(4):465-474. doi: 10.1261/rna.080347.124. RNA. 2025. PMID: 39814459 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

