The role of SOCS proteins in the development of virus- induced hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 33849568
- PMCID: PMC8045357
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-021-01544-w
The role of SOCS proteins in the development of virus- induced hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
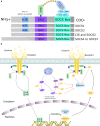
Background: Liver cancer has become one of the most common cancers and has a high mortality rate. Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most common liver cancers, and its occurrence and development process are associated with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections. Main body The serious consequences of chronic hepatitis virus infections are related to the viral invasion strategy. Furthermore, the viral escape mechanism has evolved during long-term struggles with the host. Studies have increasingly shown that suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins participate in the viral escape process. SOCS proteins play an important role in regulating cytokine signaling, particularly the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) signaling pathway. Cytokines stimulate the expression of SOCS proteins, in turn, SOCS proteins inhibit cytokine signaling by blocking the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, thereby achieving homeostasis. By utilizing SOCS proteins, chronic hepatitis virus infection may destroy the host's antiviral responses to achieve persistent infection.
Conclusions: This review provides recent knowledge regarding the role of SOCS proteins during chronic hepatitis virus infection and provides some new ideas for the future treatment of chronic hepatitis.
Keywords: Cytokine; Hepatitis virus; Hepatocellular carcinoma; JAK-STAT signaling pathway; SOCS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subcellular mislocalization of mutant hepatitis B X proteins contributes to modulation of STAT/SOCS signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.Intervirology. 2008;51(6):432-43. doi: 10.1159/000209672. Epub 2009 Mar 26. Intervirology. 2008. PMID: 19321929
-
Hepatitis B virus overexpresses suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS3) thereby contributing to severity of inflammation in the liver.Virus Res. 2010 Mar;148(1-2):51-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2009.12.003. Epub 2009 Dec 29. Virus Res. 2010. PMID: 20005910
-
Correlation between the suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 and 3 and hepatitis B virus: possible roles in the resistance to interferon treatment.Virol J. 2014 Mar 17;11:51. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-11-51. Virol J. 2014. PMID: 24636575 Free PMC article.
-
The Suppressor of Cytokine Signalling family of proteins and their potential impact on COVID-19 disease progression.Rev Med Virol. 2022 May;32(3):e2300. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2300. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Rev Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 34546610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppressors of cytokine signaling as tumor repressors. Silencing of SOCS3 facilitates tumor formation and growth in lung and liver.J BUON. 2008 Apr-Jun;13(2):263-5. J BUON. 2008. PMID: 18555475 Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity and Leptin Resistance in the Regulation of the Type I Interferon Early Response and the Increased Risk for Severe COVID-19.Nutrients. 2022 Mar 26;14(7):1388. doi: 10.3390/nu14071388. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35406000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application and progress of the detection technologies in hepatocellular carcinoma.Genes Dis. 2022 Apr 22;10(5):1857-1869. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.04.003. eCollection 2023 Sep. Genes Dis. 2022. PMID: 37492708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chinese medicine in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: The mechanisms of signal pathway regulation.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 12;10(20):e39176. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39176. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39640799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomimetics of Natural Regulators of JAK-STAT Pathway: Novel Therapeutic Perspectives.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jan 3;8:792546. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.792546. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35047557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysophosphatidylcholines Promote Influenza Virus Reproduction through the MAPK/JNK Pathway in PMA-Differentiated THP-1 Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 13;25(12):6538. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126538. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928244 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

