Radiomics analysis for predicting pembrolizumab response in patients with advanced rare cancers
- PMID: 33849924
- PMCID: PMC8051405
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001752
Radiomics analysis for predicting pembrolizumab response in patients with advanced rare cancers
Abstract
Background: We present a radiomics-based model for predicting response to pembrolizumab in patients with advanced rare cancers.
Methods: The study included 57 patients with advanced rare cancers who were enrolled in our phase II clinical trial of pembrolizumab. Tumor response was evaluated using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) 1.1 and immune-related RECIST (irRECIST). Patients were categorized as 20 "controlled disease" (stable disease, partial response, or complete response) or 37 progressive disease). We used 3D-slicer to segment target lesions on standard-of-care, pretreatment contrast enhanced CT scans. We extracted 610 features (10 histogram-based features and 600 second-order texture features) from each volume of interest. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator logistic regression was used to detect the most discriminatory features. Selected features were used to create a classification model, using XGBoost, for the prediction of tumor response to pembrolizumab. Leave-one-out cross-validation was performed to assess model performance.
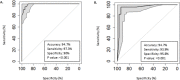
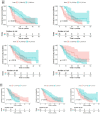
Findings: The 10 most relevant radiomics features were selected; XGBoost-based classification successfully differentiated between controlled disease (complete response, partial response, stable disease) and progressive disease with high accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity in patients assessed by RECIST (94.7%, 97.3%, and 90%, respectively; p<0.001) and in patients assessed by irRECIST (94.7%, 93.9%, and 95.8%, respectively; p<0.001). Additionally, the common features of the RECIST and irRECIST groups also highly predicted pembrolizumab response with accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and p value of 94.7%, 97%, 90%, p<0.001% and 96%, 96%, 95%, p<0.001, respectively.
Conclusion: Our radiomics-based signature identified imaging differences that predicted pembrolizumab response in patients with advanced rare cancer.
Interpretation: Our radiomics-based signature identified imaging differences that predicted pembrolizumab response in patients with advanced rare cancer.
Keywords: immunotherapy.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CN reports grant support and personal fees from General Electric Healthcare, outside the submitted work. SB reports grant support from National Institutes of Health, outside the submitted work. JRA reports personal fees from Novartis, Eli Lilly, Orion Pharmaceuticals, Servier Pharma, Peptomyc, and Merck Sharpe, on the advisory board for Novartis, Eli Lilly, Orion Pharmaceuticals, Servier Pharma, Peptomyc, Merck Sharpe & Dome, Kelun Pharma/Klus Pharma, Pfizer, Roche Pharma, and Elipses Pharma, research funding from Bayer, Novartis, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Tocagen, Symphogen, BioAtla, Pfizer, GenMab, CytomX, KELUN-BIOTECH, Takeda-Millenium, GLAXOSMITHKLINE, Ipsen, from null, outside the submitted work. VS reports clinical trial research funding from Novartis, Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, Nanocarrier, Vegenics, Celgene, Northwest Biotherapeutics, Berghealth, Incyte, Fujifilm, Pharmamar, D3, Pfizer, Multivir, Amgen, Abbvie, Alfa-sigma, Agensys, Boston Biomedical, Idera Pharma, Inhibrx, Exelixis, Blueprint medicines, Loxo oncology, Takeda and Roche/ Genentech, National Comprehensive Cancer Network, NCI-CTEP and UT MD Anderson Cancer Center, outside the submitted work. JH reports grants from Immune Deficiency Foundation, Jeffery Modell Foundatoin and Chao Physician-Scientist, and Baxalta, and has served as an advisory board member for Takeda, CSL Behring, and Horizn Pharma outside the submitted work. AN reports research support and non-financial support from Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., grants from NCI/NIH, research support from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, during the conduct of the study; grants from NCI, research support from EMD Serono, MedImmune, Healios Onc. Nutrition, Atterocor, Amplimmune, ARMO BioSciences, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Incyte, Novartis, Regeneron, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, CytomX Therapeutics, Neon Therapeutics, Calithera BioSciences, TopAlliance BioSciences, Eli Lilly, Kymab, PsiOxus, Arcus Biosciences, NeoImmuneTech, ImmuneOncia, and Surface Oncology, non-financial support for travel and accommodation from ARMO BioSciences, and has served as an advisory board member for Novartis, CytomX Therapeutics, Genome and Company, STCube Pharmaceuticals, OncoSec KEYNOTE-695, and Kymab outside the submitted work. RRC, CR, MAk, MAyoub, SA, NE, PM, POZ, RV, CP, BS, DDK declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Letter to the editor: radiomics analysis for predicting pembrolizumab response in patients with advanced rare cancers.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jul;9(7):e003044. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003044. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34315822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Institute NC . Cancer STAT facts. Surveilance, epidemiology, and end results program, 2020. Available: https://seercancergov/statfacts/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
