Prognostic impact of early tumor shrinkage and depth of response in patients with microsatellite instability-high metastatic colorectal cancer receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors
- PMID: 33849927
- PMCID: PMC8051394
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002501
Prognostic impact of early tumor shrinkage and depth of response in patients with microsatellite instability-high metastatic colorectal cancer receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are the new standard of care in microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H)/deficient mismatch repair (dMMR) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Since tumor response dynamic parameters already shown a strong association with survival outcomes in patients with mCRC treated with first-line therapy, we investigated the association of early tumor shrinkage (ETS) and depth of response (DoR) in patients with MSI-H/dMMR mCRC treated with ICIs.
Methods: This is a retrospective, multicenter, cohort study in patients with dMMR and/or MSI-high mCRC treated with ICIs (anti-PD-1/PD-L1 with or without anti-CTLA-4 agents) with measurable disease and at least one post-baseline radiological disease reassessment. The Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional-hazards regression models were used for survival analyses. A maximally selected statistics method in a Cox regression model for progression-free survival (PFS) was used to determine the optimal cut-offs for ETS and DoR.
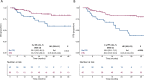
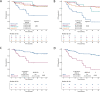
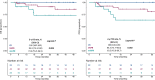
Results: We included a total of 169 patients: 116 (68.6%) were treated with anti-PD-1 monotherapy, whereas 53 (31.4%) with anti-PD-1 plus anti-CTLA-4 agents. Patients with primary progressive disease (N=37, 21.9%), experienced an extremely poor overall survival (OS) and were evaluated separately. In patients with clinical benefit, we observed a significant association between ETS and DoR with both OS and PFS, and we identified a relative reduction of at least 1% as the optimal cut-off for ETS and a relative reduction of at least 50% as the optimal cut-off for DoR.
Conclusions: ETS and DoR are important prognostic factors in patients with MSI-high mCRC treated with ICIs that might be useful to design treatment intensification/deintensification strategies. A prospective validation of both is warranted.
Keywords: gastrointestinal neoplasms; immunotherapy; tumor biomarkers.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: GC reports the following competing interests outside the present work: advisory board member of Novartis, Roche, Lilly, Daichi-Sankyo, Astra Zeneca, Veracyte and Genomic Health; scientific advisor for Ellipsis. All the remaining authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor from Colle et al.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jun;9(6):e002997. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002997. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34162716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Overman MJ, McDermott R, Leach JL, et al. . Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (CheckMate 142): an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 2017;18:1182–91. 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30422-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- NCCN . Clinical practice Guidelies in oncology, version 2, 2021. Available: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/colon.pdf
-
- Cremolini C, Loupakis F, Antoniotti C, et al. . Early tumor shrinkage and depth of response predict long-term outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with first-line chemotherapy plus bevacizumab: results from phase III tribe trial by the Gruppo Oncologico del Nord Ovest. Ann Oncol 2015;26:1188–94. 10.1093/annonc/mdv112 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
