Is IL-6 a key cytokine target for therapy in COVID-19?
- PMID: 33850327
- PMCID: PMC8043092
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-021-00553-8
Is IL-6 a key cytokine target for therapy in COVID-19?
Abstract
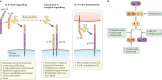
The identification of elevated IL-6 levels in patients with severe COVID-19 led to the rapid development of clinical trials targeting this cytokine. Overall, these trials do not support the widespread use of IL-6 antagonists in hospitalized patients with mild-to-moderate disease, but IL-6 antagonists may be beneficial when rapidly deployed in patients with severe COVID-19, as we discuss here.
Conflict of interest statement
S.A.J. has received research support from GSK, Mestag Therapeutics, Hoffmann la Roche, NovImmune SA, and Ferring Pharmaceuticals, and consultancy from Sanofi-Regeneron, GSK, Janssen, EUSA Pharmaceuticals, NovImmune SA., Chugai Pharmaceutical and Hoffmann la Roche. C.A.H. has received research support from Janssen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Role of Tocilizumab in SARS-CoV-2-Induced Cytokine Storm: Rationale and Current Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 17;22(6):3059. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063059. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The COVID-19 Cytokine Storm; What We Know So Far.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 16;11:1446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01446. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32612617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunopathogenesis and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(1):316-329. doi: 10.7150/thno.49713. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of IL-6 inhibitor in treatment of COVID-19-related cytokine release syndrome.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 21;18(6):1356-1362. doi: 10.7150/ijms.53564. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33628091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Importance of the Timing of Tocilizumab Administration in Moderate to Severely Ill COVID-19: Single Centered Experience Case series.Acta Med Indones. 2021 Jul;53(3):319-325. Acta Med Indones. 2021. PMID: 34611072
Cited by
-
Pathway-Based Mendelian Randomization for Pre-Infection IL-6 Levels Highlights Its Role in Coronavirus Disease.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jul 6;15(7):889. doi: 10.3390/genes15070889. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062668 Free PMC article.
-
Subcutaneous IL-6 Inhibitor Sarilumab vs. Standard Care in Hospitalized Patients With Moderate-To-Severe COVID-19: An Open Label Randomized Clinical Trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 23;9:819621. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.819621. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35280907 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist Treatment on ACE2 Expression and SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Primary Airway Epithelial Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 19;12:765951. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.765951. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867390 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SARS-CoV-2 -induced cytokines and growth factors in coagulopathy and thromboembolism.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022 Feb;63:58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2021.10.007. Epub 2021 Oct 24. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022. PMID: 34750061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Acupuncture for Long COVID: Mechanisms and Models.Med Acupunct. 2022 Jun 1;34(3):159-166. doi: 10.1089/acu.2021.0090. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Med Acupunct. 2022. PMID: 35832109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soin AS, et al. Tocilizumab plus standard care versus standard care in patients in India with moderate to severe COVID-19-associated cytokine release syndrome (COVINTOC): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021 doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00081-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

