Differences between myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA) and proteinase 3-ANCA associated vasculitis: A retrospective study from a single center in China
- PMID: 33850533
- PMCID: PMC8027729
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.9993
Differences between myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA) and proteinase 3-ANCA associated vasculitis: A retrospective study from a single center in China
Abstract
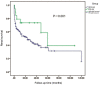
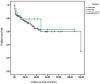
In antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitides (AAV), the two major target antigens of ANCA are proteinase 3 (PR3) and myeloperoxidase (MPO). Evidence is accumulating that there are distinct differences between patients with PR3-AAV and those with MPO-AAV. In the present study, the clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients with PR3-AAV and MPO-AAV from a single center in China were retrospectively analyzed. A total of 212 Chinese patients with AAV were recruited in the present study; 189/212 (89.15%) patients were classified as having MPO-AAV and 23/212 (10.85%) patients as having PR3-AAV. Compared with those in the PR3-AAV group, patients in the MPO-AAV group were older and less frequently had ear, nose and throat or ophthalmic involvement. MPO-AAV patients had higher levels of serum creatinine and proteinuria at baseline. No significant difference was observed with regard to the pathological changes of the glomeruli and tubulointerstitium between the two groups. The probability of developing end-stage renal disease was significantly higher in patients with MPO-AAV compared with that in patients with PR3-AAV. There was no significant difference in the one-year patient survival rate between the two groups. However, differences in certain clinical characteristics and outcomes were observed between MPO-AAV and PR3-AAV patients. A large national investigation of AAV is required to confirm the concept that PR3-AAV and MPO-AAV are distinct disease entities.
Keywords: antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody; clinicopathological features; myeloperoxidase; prognosis; proteinase 3.
Copyright: © Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical features and prognosis of ANCA-associated vasculitis patients who were double-seropositive for myeloperoxidase-ANCA and proteinase 3-ANCA.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Apr 2;24(1):66. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01318-y. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38564029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloperoxidase-ANCA-positive granulomatosis with polyangiitis is a distinct subset of ANCA-associated vasculitis: A retrospective analysis of 455 patients from a single center in China.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Feb;48(4):701-706. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.05.003. Epub 2018 May 9. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019. PMID: 29887327
-
Clinical characteristics of patients with vasculitis positive for anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody targeting both proteinase 3 and myeloperoxidase: a retrospective study.Rheumatol Int. 2019 Nov;39(11):1919-1926. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04447-w. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Rheumatol Int. 2019. PMID: 31552433
-
Relevance of Combined Clinicopathologic Phenotype and Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody Serotype in the Diagnosis of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody Vasculitis.Kidney Int Rep. 2022 Sep 20;7(12):2676-2690. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.09.011. eCollection 2022 Dec. Kidney Int Rep. 2022. PMID: 36506241 Free PMC article.
-
Proteinase 3-ANCA Vasculitis versus Myeloperoxidase-ANCA Vasculitis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Oct;26(10):2314-27. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014090903. Epub 2015 May 8. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25956510 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Systematic Review.Biology (Basel). 2022 Dec 6;11(12):1767. doi: 10.3390/biology11121767. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Falk RJ, Jennette JC. ANCA small-vessel vasculitis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:314–322. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
