Alliin inhibits adipocyte differentiation by downregulating Akt expression: Implications for metabolic disease
- PMID: 33850535
- PMCID: PMC8027764
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.9995
Alliin inhibits adipocyte differentiation by downregulating Akt expression: Implications for metabolic disease
Abstract
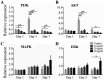
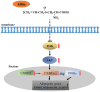
Obesity is currently an important health problem and is associated with an increased likelihood of various diseases. The efficacies of various natural treatments have been assessed for their utility in treating obesity. Alliin (S-allyl-L-cysteine sulfoxides) is considered the major component of garlic and has a wide range of natural antioxidant properties. However, the direct effects of alliin on obesity have not been well clarified. The present study investigated the effects and possible mechanisms of alliin on adipocyte differentiation. The 3T3-L1 cells were treated with alliin (0-40 µg/ml) during adipogenic differentiation. The effect of alliin on lipid accumulation was evaluated by Oil red O staining. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR was performed to investigate the expression levels of adipogenic differentiation-related genes. The accumulation of lipid droplets was markedly inhibited following alliin treatment. The expression levels of multiple adipogenic transcription markers, such as CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) β, C/EBP α and peroxisome proliferation-activity receptor γ, were markedly decreased following treatment with alliin during adipogenic differentiation. Expression levels of several adipocyte-related genes were subsequently suppressed. Additionally, alliin suppressed PKB/Akt and PI3K expression. These results suggested that alliin exhibits anti-adipogenic activity by downregulating major adipogenic differentiation-related genes and Akt/PI3K expression. Alliin may have a potential therapeutic effect on metabolic disease.
Keywords: Akt; CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β; adipogenesis; alliin; metabolic disease; peroxisome proliferation-activity receptor γ.
Copyright: © Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

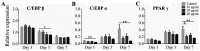
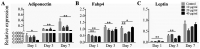
Similar articles
-
Anti-adipogenic effect of epiberberine is mediated by regulation of the Raf/MEK1/2/ERK1/2 and AMPKα/Akt pathways.Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Dec;38(12):2153-62. doi: 10.1007/s12272-015-0626-3. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Arch Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 26119076
-
Suppression of adipocyte differentiation and lipid accumulation by stearidonic acid (SDA) in 3T3-L1 cells.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Sep 25;16(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0574-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28946872 Free PMC article.
-
α, β-Amyrin, a pentacyclic triterpenoid from Protium heptaphyllum suppresses adipocyte differentiation accompanied by down regulation of PPARγ and C/EBPα in 3T3-L1 cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:1860-1866. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.027. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551441
-
Coptis chinensis alkaloids exert anti-adipogenic activity on 3T3-L1 adipocytes by downregulating C/EBP-α and PPAR-γ.Fitoterapia. 2014 Oct;98:199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2014.08.006. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Fitoterapia. 2014. PMID: 25128422
-
7,8-Dihydroxyflavone inhibits adipocyte differentiation via antioxidant activity and induces apoptosis in 3T3-L1 preadipocyte cells.Life Sci. 2016 Jan 1;144:103-12. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.11.028. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26631505
Cited by
-
Elucidating Drug-Like Compounds and Potential Mechanisms of Corn Silk (Stigma Maydis) against Obesity: A Network Pharmacology Study.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021 Nov 6;43(3):1906-1936. doi: 10.3390/cimb43030133. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34889899 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic effects of natural organosulfur compounds on atherosclerosis and their potential mechanisms: a comprehensive review.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 1;12:1599154. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1599154. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40666422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protopanaxadiol-Enriched Rice Exerted Antiadipogenic Activity during 3T3-L1 Differentiation and Anti-Inflammatory Activity in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 11;15(8):2123. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082123. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631337 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Modulation of Adipogenesis and Apoptosis by PPARG Agonist Rosiglitazone and Antagonist Betulinic Acid in 3T3-L1 Cells.Biomedicines. 2025 May 30;13(6):1340. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061340. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564064 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Garlic Skin Based on Metabolomics Analysis in the Meat Quality of Black Goats.Foods. 2025 May 28;14(11):1911. doi: 10.3390/foods14111911. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40509439 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
