Ginkgo biloba delays light-induced photoreceptor degeneration through antioxidant and antiapoptotic properties
- PMID: 33850548
- PMCID: PMC8027744
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10008
Ginkgo biloba delays light-induced photoreceptor degeneration through antioxidant and antiapoptotic properties
Abstract
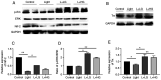
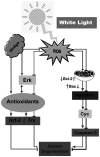
Intense exposure to artificial bright light increases the risk of retinal damage resulting in blurred vision and blindness. Long-term exposure to bright light elevates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis, which results in photoreceptor cell degeneration. However, to the best of our knowledge, the molecular mechanism associated with light-induced retinopathy remains unclear. In the present study, the mechanisms involved in light-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis were investigated along with the protective effects of Ginkgo biloba (EGb 761) in photoreceptor cell degeneration. EGb 761 was administered to mice at a dose of 50 or 100 mg/kg for 7 days prior to exposure to bright light (5,000 lux for 24 h). Furthermore, photoreceptor cell disorders were evaluated using electroretinogram (ERG) and H&E staining analyses. The expression levels of antioxidant genes and proteins ERK, thioredoxin (Trx) and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf-2) and the induction of apoptosis cytochrome c (Cyc), cleaved caspase-3 and Bax, were determined by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and western blotting. ERG and histological analysis revealed that exposure to bright light induced functional and morphological changes to the photoreceptor cells. Exposure to bright light increased the levels of Cyc, cleaved caspase-3 and Bax, and decreased the levels of phosphorylated (p-) Erk, Nrf-2 and thioredoxin (Trx). However, treatment of mice with EGb 761 increased the expression levels of antiapoptotic (Bcl-2) and antioxidant (p-Erk, Trx and Nrf-2) proteins and decreased the expression levels of the apoptotic genes (Cyc, cleaved caspase-3 and Bax). Based on these findings, the present study suggested that prolonged exposure to light induces photoreceptor cell degeneration, where EGb 761 treatment may serve a therapeutic effect on the development of photoreceptor cell degeneration.
Keywords: Ginkgo biloba; apoptosis; light damage; oxidative stress; retinal degeneration.
Copyright © 2021, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The therapeutic potential of sulforaphane on light-induced photoreceptor degeneration through antiapoptosis and antioxidant protection.Neurochem Int. 2016 Nov;100:52-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.08.011. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27567738
-
Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper Protects the Retina From Light-Induced Retinal Degeneration by Inducing Bcl-xL in Rats.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Jul 1;58(9):3656-3668. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22116. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28728173
-
Ginkgo biloba Extract Attenuates Light-Induced Photoreceptor Degeneration by Modulating CAV-1-Redoxosome Signaling.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;11(7):1268. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071268. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883759 Free PMC article.
-
[Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761). State of knowledge in the dawn of the year 2000].Ann Pharm Fr. 1999 Jul;57 Suppl 1:1S8-88. Ann Pharm Fr. 1999. PMID: 10481350 Review. French.
-
Molecular mechanisms of light-induced photoreceptor apoptosis and neuroprotection for retinal degeneration.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2005 Mar;24(2):275-306. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2004.08.002. Epub 2004 Nov 11. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2005. PMID: 15610977 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism and ingredients prediction of Radix Salviae-Angelicae Sinensis Radix-Lycii Fructus-Rehmanniae Radix Praeparata-Ginkgo Folium for retinitis pigmentosa therapy using network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Oct 25;11(11):382. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3557. Epub 2023 Oct 7. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37970593 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgo biloba: A Leaf of Hope in the Fight against Alzheimer's Dementia: Clinical Trial Systematic Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 27;13(6):651. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060651. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929090 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kong L, Liu B, Zhang C, Wang B, Wang H, Song X, Yang Y, Ren X, Yin L, Kong H, Ma H. The therapeutic potential of sulforaphane on light-induced photoreceptor degeneration through antiapoptosis and antioxidant protection. Neurochem Int. 2016;100:52–61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.08.011. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
