The effect of pregabalin on postdural puncture headache among patients undergoing elective cesarean section: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 33850624
- PMCID: PMC8022150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102226
The effect of pregabalin on postdural puncture headache among patients undergoing elective cesarean section: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Post-dural puncture headache (PDPH) is one of the most common problems of cesarean section. The present study aimed to evaluate the effect of pregabalin on PDPH among patients undergoing elective cesarean section.
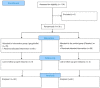
Materials and methods: This double-blind clinical trial was performed on 136 patients undergoing elective cesarean section referred to Shahid Motahari Teaching Hospital in Urmia in northwestern Iran from February 1 to December 20, 2020. Patients were selected by convenience sampling method and randomly divided into two groups of intervention and control (N = 68 people each group). The presence of PDPH and its severity were recorded in the checklist based on the VAS, and conventional treatments were prescribed in the case of occurrence of the PDPH. The PDPH severity was also assessed by the patient using the 10-cm Visual Analog Scale (VAS).
Results: The mean age of participants was 27.82 years. A total of 29 people suffered from hypotension. Regarding pain severity, the mean pain score in the intervention group was significantly lower than the control group (p = 0.01). Results also showed that the frequency of PDPH in the intervention group was significantly lower than the placebo group (4.4% vs. 11.8%; p = 0.019). There was no significant difference between intervention and control groups in terms of demographic characteristics (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Results of the present study showed the use of oral pregabalin at night before spinal anesthesia in patients undergoing elective cesarean(C-) section had a preventive effect on the severity and incidence of PDPH.
Keywords: Cesarean section; Pain; Post-dural puncture headache; Pregabalin.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of ondansetron on post-dural puncture headache (PDPH) in parturients undergoing cesarean section: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study.J Anesth. 2015 Oct;29(5):702-7. doi: 10.1007/s00540-015-2000-5. Epub 2015 Mar 27. J Anesth. 2015. PMID: 25812804 Clinical Trial.
-
Prophylactic effect of chamomile on post-dural puncture headache in women undergoing elective cesarean section: A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.Explore (NY). 2024 May-Jun;20(3):424-429. doi: 10.1016/j.explore.2023.10.009. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Explore (NY). 2024. PMID: 37926605 Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized study to evaluate post-dural puncture headache after cesarean section: Comparison with median and paramedian approaches.Niger J Clin Pract. 2019 Nov;22(11):1564-1569. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_100_19. Niger J Clin Pract. 2019. PMID: 31719278 Clinical Trial.
-
Dexamethasone and post-dural puncture headache in women who underwent cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia: A systemic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021 Jan 18;62:104-113. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.01.024. eCollection 2021 Feb. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33520204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and associated factors of post dural puncture headache among parturients who underwent cesarean section with spinal anesthesia: A systemic review and meta-analysis, 2021.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021 Jun 2;66:102456. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102456. eCollection 2021 Jun. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34141426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Does Preoperative Coffee Consumption Prevent Intraoperative Hypotension in Cesarean Section Surgeries?Cureus. 2024 Jul 1;16(7):e63584. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63584. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39087173 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment and Prevention of Post-dural Puncture Headaches: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 Jan 15;16(1):e52330. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52330. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38361721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Sumatriptan, Theophylline, Pregabalin and Caffeine on Prevention of Headache Caused By Spinal Anaesthesia (PDPH): A Systematic Review.J West Afr Coll Surg. 2022 Oct-Dec;12(4):102-116. doi: 10.4103/jwas.jwas_183_22. Epub 2022 Nov 23. J West Afr Coll Surg. 2022. PMID: 36590776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of pharmacological therapies for preventing post-dural puncture headaches in obstetric patients: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Mar 29;23(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-05531-7. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 36991366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boerma T., Ronsmans C., Melesse D.Y., Barros A.J., Barros F.C., Juan L., Moller A.-B., Say L., Hosseinpoor A.R., Yi M. Global epidemiology of use of and disparities in caesarean sections. Lancet. 2018;392(10155):1341–1348. - PubMed
-
- Miller R.D., Eriksson L., Fleisher L.A., Wiener-Kronish J.P., Young W.L. Miller's Anesthesia. 2010. Miller's anesthesia. 2827-2827.
-
- Choi P.T., Galinski S.E., Takeuchi L., Lucas S., Tamayo C., Jadad A.R. PDPH is a common complication of neuraxial blockade in parturients: a meta-analysis of obstetrical studies. Can. J. Anesth. 2003;50(5):460–469. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources