Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Potential Use in Nanomedicine
- PMID: 33850629
- PMCID: PMC7610589
- DOI: 10.3390/app10155194
Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Potential Use in Nanomedicine
Abstract
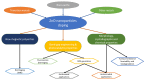
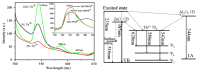
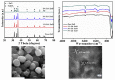
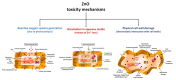
Smart nanoparticles for medical applications have gathered considerable attention due to an improved biocompatibility and multifunctional properties useful in several applications, including advanced drug delivery systems, nanotheranostics and in vivo imaging. Among nanomaterials, zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) were deeply investigated due to their peculiar physical and chemical properties. The large surface to volume ratio, coupled with a reduced size, antimicrobial activity, photocatalytic and semiconducting properties, allowed the use of ZnO NPs as anticancer drugs in new generation physical therapies, nanoantibiotics and osteoinductive agents for bone tissue regeneration. However, ZnO NPs also show a limited stability in biological environments and unpredictable cytotoxic effects thereof. To overcome the abovementioned limitations and further extend the use of ZnO NPs in nanomedicine, doping seems to represent a promising solution. This review covers the main achievements in the use of doped ZnO NPs for nanomedicine applications. Sol-gel, as well as hydrothermal and combustion methods are largely employed to prepare ZnO NPs doped with rare earth and transition metal elements. For both dopant typologies, biomedical applications were demonstrated, such as enhanced antimicrobial activities and contrast imaging properties, along with an improved biocompatibility and stability of the colloidal ZnO NPs in biological media. The obtained results confirm that the doping of ZnO NPs represents a valuable tool to improve the corresponding biomedical properties with respect to the undoped counterpart, and also suggest that a new application of ZnO NPs in nanomedicine can be envisioned.
Keywords: antibacterial properties; bioimaging; doped ZnO; drug delivery; rare earth; theranostics; transition metals; zinc oxide nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Efficacy of Fe-, Co-, and Mn-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles.Molecules. 2024 Dec 18;29(24):5966. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245966. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39770055 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as a Promising Nanomedicine Approach for Anticancer, Antibacterial, and Anti-Inflammatory Therapies.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 7;20:4299-4317. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S507214. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40225223 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Sulfur Doping and Temperature on the Energy Bandgap of ZnO Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Activities.ACS Omega. 2022 Mar 15;7(12):10796-10803. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00647. eCollection 2022 Mar 29. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35382288 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress of rare earth doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles: Luminescence properties, synthesis and biomedical applications.Acta Biomater. 2022 Aug;148:22-43. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.06.006. Epub 2022 Jun 5. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35675891 Review.
-
Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications - A Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Dec 3;19:12889-12937. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S487188. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39651353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Photoluminescent neodymium-doped ZnO nanocrystals prepared by laser ablation in solution for NIR-II fluorescence bioimaging.Heliyon. 2022 May 29;8(6):e09554. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09554. eCollection 2022 Jun. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35677401 Free PMC article.
-
Iron-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Nanoplatforms for Theranostics.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Oct 6;11(10):2628. doi: 10.3390/nano11102628. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685064 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenic Ag-doped ZnO nanostructures induced cytotoxicity in luminal A and triple-negative human breast cancer cells.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024;19(29):2479-2493. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2024.2347825. Epub 2024 May 29. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39466383 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesized Magnetic Nanoparticles as Effective Nanosupport for the Immobilization of Lipase: Application for the Synthesis of Lipophenols.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Feb 11;11(2):458. doi: 10.3390/nano11020458. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670153 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced antibacterial and anticancer activities of plant extract mediated green synthesized zinc oxide-silver nanoparticles.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 24;14:1194292. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1194292. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37577438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raza A, Hayat U, Rasheed T, Bilal M, Iqbal HMN. “Smart” materials-based near-infrared light-responsive drug delivery systems for cancer treatment: A review. J Mater Res Technol. 2019;8:1497–1509. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.03.007. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
